In the context of general relativity, time slows down in curved space-time. This is referred to as _____
A) spatial loss
B) spatial growth
C) time dilation
D) time fragmentation
C
You might also like to view...
When I was a teenager, I saw a Candid Camera sequence in which they filmed a person struggling with a suitcase that (unknown to that person) contained a large and rapidly spinning gyroscope. Imagine you are carrying such a suitcase where the gyroscope’s angular velocity is oriented horizontally to your right as you carry it in your right hand. Imagine you try to make a left turn, thus turning the suitcase to the left around a vertical axis. What does the suitcase do?
A. It turns to the left as one would expect. B. It tries to turn instead to the right. C. It tries to rotate around a horizontal axis, with its right face turning upward. D. It tries to rotate around a horizontal axis, with its left face turning upward. E. It tries to rotate around a rightward axis, with its front edge moving up.
A particle whose mass is 2.0 kg moves in the xy plane with a constant speed of 3.0 m/s along the direction 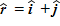
A.
B.
C.
D.
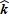
E.
Identify at least three patterns of motion or planetary arrangement/location that a theory of solar system formation should be able to explain.
What will be an ideal response?
An excited atom decays to its ground state and emits a photon of red light. If instead the decay is to an intermediate state, then the light emitted could be
A) red. B) violet. C) blue. D) any of these E) none of these