For a price change from P1 to P2 the change in quantity demanded is from Q1 to Q2 and price elasticity of demand would be
a. [(P1–P2)/(P1+P2)] / [(Q1-Q2)/(Q1+Q2)]
b. [(P1+P2)/(P1-P2)] / [(Q1+Q2)/(Q1-Q2)]
c. [(Q1-Q2)/(Q1+Q2)]/2 / [(P1–P2)/(P1+P2)]/2
d. [(Q1+Q2)/(Q1-Q2)] / [(P1+P2)/(P1-P2)]
e. [(Q1+Q2)/(Q1-Q2)/2] / [(P1+P2)/(P1-P2)/2]
C
You might also like to view...
Diminishing returns to capital is a consequence of firms' incentives to use each piece of capital as productively as possible and illustrates the:
A. cost-benefit principle. B. principle of comparative advantage. C. principle of increasing opportunity costs. D. scarcity principle.
The poverty rate in the United States has __________ over the last 30 years.
A. remained the same B. increased C. decreased D. not been accurately measured
Figure 18-3
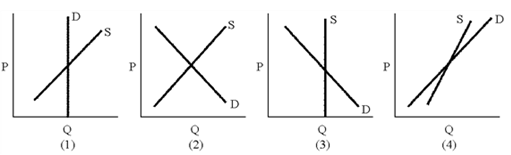
A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4
A good time for an American to hold German stocks, ceteris paribus, is when the
A. Euro is stable compared to the U.S. dollar. B. The return in the German stock market has no relationship to the value of the dollar compared to the euro. C. U.S. dollar appreciates in value compared to the euro. D. U.S. dollar depreciates in value compared to the euro.