Suppose an engineer suggests that air instead of water could flow through the tube and the velocity of the air could be increased until the heat transfer coefficient with the air equals that obtained with water at 1.5 m/s. Determine the velocity required and comment on the feasibility of the engineer’s suggestion. Note that the speed of sound in air at 100°C is 387 m/s.
GIVEN
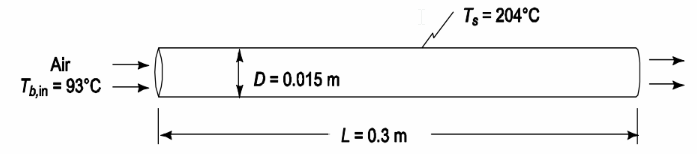
• Air flow through a tube
• Bulk inlet air temperature (Tb,in) = 93°C
• Tube diameter (D) = 0.015 m
• Tube length (L) = 0.3 m
• Tube surface temperature (Ts) = 204°C
• From Problem 7.32: h ,c L = 13,037 W/(m2 K)
FIND
• The velocity (V) required to obtain h ,c L = 13,037 W/(m2 K)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state
• Constant and uniform tube temperature
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for dry air at the inlet bulk temperature of 93°C
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0302 W/(m K)
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 22.9 × 10–6 m2/s
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71
The flow must be turbulent, therefore, the heat transfer coefficient of the fully developed case must be
13,037 W/(m2 K) Therefore, the Nusselt number is
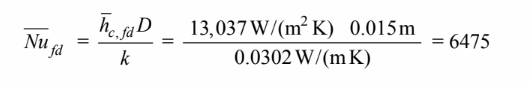
Applying the Dittus-Boelter correlation
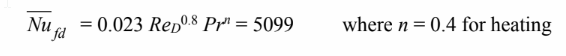
Solving for the Reynolds number
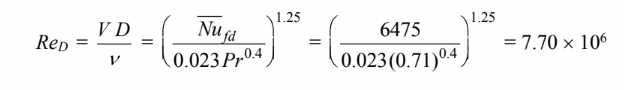
Solving for the velocity
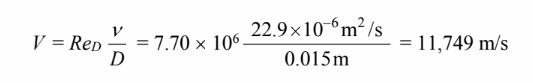
This velocity is obviously unrealistic because it corresponds to a Mach number of 30. Under such
conditions when the speed of sound is reached, a shock wave will form and choke the flow.
You might also like to view...
A 12.0 V battery is placed across a 4.00 resistor. If the current through the resistor is 2.80 A, what is the terminal voltage of the battery?
resistor. If the current through the resistor is 2.80 A, what is the terminal voltage of the battery?
A. 12.0 V B. 12.8 V C. 11.6 V D. 11.2 V E. 9.6 V
Light with a wavelength of 310 nm is incident on a metal that has a work function of 3.8 eV. What is the maximum kinetic energy that a photoelectron ejected in this process can have?
A) 0.62 × 10-19 J B) 0.21 × 10-19 J C) 0.36 × 10-19 J D) 0.48 × 10-19 J E) 0.33 × 10-19 J
Consider two containers with the same volume and temperature. Container One holds "dry" air (a mixture of nitrogen and oxygen). Container Two holds "moist" air. The "moist" air has the same ratio of nitrogen to oxygen molecules but also contains water vapor. According to the ideal gas law, if the pressures are equal, the weight of the gas in Container One will be:
a. lighter than the gas inside the second container. b. equal to the weight of the gas in the second container. c. heavier than the gas inside the second container. d. all the above are incorrect because the pressures cannot be equal.
An object of unknown weight is suspended as shown. The tension in rope 1 is 25 lb, and the tension in rope 2 is 31 lb. What is the weight of the suspended object?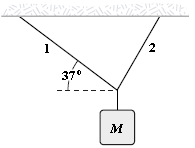
A. 36 lb B. 33 lb C. 41 lb D. 39 lb E. 56 lb