The cell walls of fungi are composed mainly of
a. hyphae.
b. cellulose.
c. chitin.
d. phospholipids.
e. mycelia.
C
You might also like to view...
Proteins are three dimensional molecules made of strands of amino acids (imagine a ball of string). There are 20 different amino acids used in proteins found in living organisms. Some of these amino acids are polar and others are non-polar. Where would a series of non-polar amino acids most likely be located in a protein that is found in the cytosol of an animal cell?
A. On the surface of the protein B. In the interior of the protein C. At the very top of the protein D. At the very bottom of the protein
Newborn humans face thermoregulatory challenges as do small mammals. One mechanism they use to generate heat is
A. nonshivering thermogenesis in "brown fat." B. evaporation in "brown fat." C. radiation in "brown fat." D. convection in "brown fat." E. shivering thermogenesis in "brown fat."
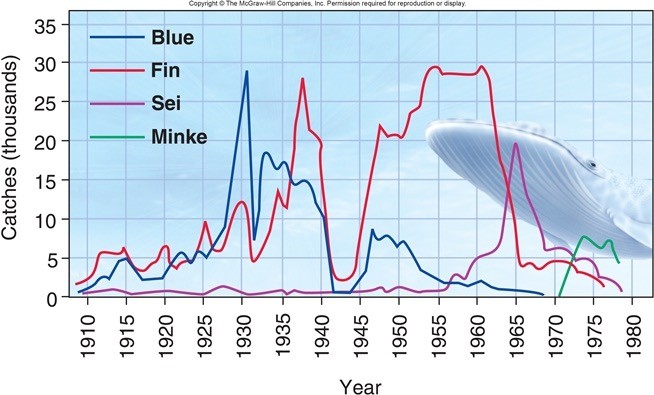 Fishing by humans has severely affected populations of many different marine species, including whales. Examine the figure above, making sure to note what each axis represents. What can best explain the pattern for minke whales?
Fishing by humans has severely affected populations of many different marine species, including whales. Examine the figure above, making sure to note what each axis represents. What can best explain the pattern for minke whales?
A. Minke whales were too difficult to catch until they become malnourished due to exploitation competition by other whales. B. Minke whale populations were overfished in the early 1900s, then recovered in the 1970s as their competitors were killed off. C. Minke whales are a new species that evolved during the 1960s as an ecological niche opened up. D. Commercial whalers did not pursue minke whales until the more valuable whale species had declined.
It has been decided, by a group of scientific experts, that lack of internal temperature regulation, presence of waterproof skin made of scales, and a waterproof egg are the three main characteristics that should be used to classify organisms as
reptiles. This decision is most consistent with: A) natural selection. B) adaptive radiation. C) cladistic taxonomy. D) classical taxonomy.