In a sensor network, the energy consumed by different functions by a sensor is as follows:
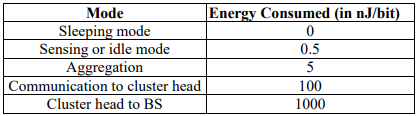
Assume the total number of nodes as P, the number of cluster heads to be m, the number of sensor nodes which send their data to different cluster heads as n, and the frame size to be B bits.
(a) Find the power consumption, during a frame time period if sensing and communication is done during every frame, assuming the other half of the nodes are sleeping at that time.
(b) Find the power consumption in the idle frame when sensing and
communication to the CH is done in every alternate frame. Remember that power is consumed even in the sleeping mode of the cycles, when sensing is not carried out.
(c) Find the total power consumption in different frames if sensing is done every other cycle, while transmission to CH is done every fourth frame.
(d) Repeat part (b) if there are 10 clusters, with each cluster consisting of 8 sensor nodes and aggregation done by CH every 8 frames while CH to base station communication takes place every 16 frames.
In a sensor network, the energy consumed by different functions by a sensor, is as follows:
-Sleeping mode is 0:
-Sensing mode is 0:5:
-Aggregation is 5:
-Communication to cluster head is 100:
-Cluster head to BS is 1000:
-Energy consumed is in nJ/bit.
Assume total number of nodes is P.
Assume number of non-cluster nodes is N.
Assume number of cluster heads is M.
Assume size of frame in bits is B.
(a) Sensing and communication is done during every frame, assuming other half nodes are sleeping at that time. Assuming that half of both cluster and non-cluster nodes are active at any time. Therefore, the power consumption during a frame time period is
0:5 *(N +M) * 0:5 + 5 * 0.5 *M + (0.5 * N *100 + 1000 *M) *B
= 0.25 *N + 2.75 *M + 50 * N * B + 1000 *M * B:
(b) Sensing and communication to CH is done in every alternate frame.
Remember that power is consumed even in sleeping mode of the
cycles, when sensing is not carried out. Therefore, the power consumption in the idle frame is 5 *(N +M).
(c) There are 4 types of frames
Idle frames: 5 *(N +M) or 500 nJ
Sensing frames: 0.5 *(N +M) or 50 nJ (When the sensing and transmission do not coincide)
Transmission frames: 100 * N * B (When the sensing and transmission do not coincide)
Sensing and transmission frames: 0.5*(N +M)+100*(N +M) (When the
sensing and transmission do coincide)
(d) There are 4 kinds of sensing frames
Sensing frames: 0.5 * (N +M) or 40 nJ (When the sensing, aggregation and transmission do not happen)
Sensing frames with aggregation: 0.5 *M + 5 *M = 5.5 *M or 27.5 nJ
(Only the cluster heads before sending to BS)
Sensing frames with communication to BS:
0.5 *M + 1000 *M or 5002:5 nJ
Sensing frames with aggregation and communication to BS:
0.5*M + 1000*M + 50*B or 10005 nJ +50* B nJ.
You might also like to view...
You terminate statements in structured text with the ____________________ character.
What will be an ideal response?What will be an ideal response?
In a cell, the nucleus is surrounded by the ____________________
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
The most common method of support is by concrete columns with ____.
A. wooden footings B. metal post anchors C. metal beams D. natural stone
A major disadvantage of the Mask-Programmed ROM (MROM) is that it:
A) is time consuming to change the stored data when system requirements change. B) is very expensive to change the stored data when system requirements change. C) cannot be reprogrammed if the stored data needs to be changed. D) has an extremely short life expectancy and requires frequent replacement.