When the money market is drawn with the value of money on the vertical axis, long-run equilibrium is obtained when the quantity demanded and quantity supplied of money are equal due to adjustments in
a. nominal interest rates.
b. real interest rates.
c. the price level.
d. the money supply.
c
You might also like to view...
Economics is best defined as the social science that studies
A) how a person can get everything he or she wants. B) how choices made in the social interest must conflict with choices made in the self-interest. C) the way to eliminate choices in our decisions. D) the choices that societies, and the people and institutions that make up societies, make in dealing with the issue of scarcity. E) the reason money exists.
If the statistical discrepancy is zero, in order to calculate GDP from the value of net domestic product at factor cost, we must add
A) the value of intermediate goods and subtract the value of imports. B) direct taxes, subtract corporate profit, and add investment. C) indirect taxes, subtract subsidies, and add depreciation. D) subsidies, subtract indirect taxes and depreciation. E) indirect taxes, subsidies, and depreciation.
Initially, the economy is in long-run equilibrium. The aggregate demand curve then shifts $80 billion to the left. The government wants to change spending to offset this decrease in demand. The MPC is 0.75 . Suppose the effect on aggregate demand of a tax change is 3/4 as strong as the effect of a change in government expenditure. There is no crowding out and no accelerator effect. What should
the government do if it wants to offset the decrease in real GDP? a. Raise both taxes and expenditures by $80 billion dollars. b. Raise both taxes and expenditures by $10 billion dollars. c. Reduce both taxes and expenditures by $80 billion dollars. d. Reduce both taxes and expenditures by $10 billion dollars.
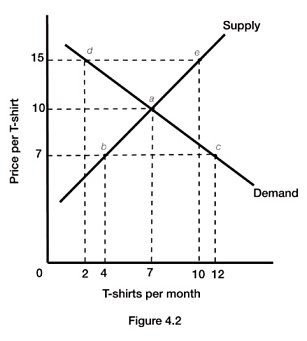 Figure 4.2 illustrates the supply and demand for t-shirts. If the actual price of t-shirts is $15, there is an:
Figure 4.2 illustrates the supply and demand for t-shirts. If the actual price of t-shirts is $15, there is an:
A. excess demand of 8 t-shirts. B. excess supply of 8 t-shirts. C. excess demand of 10 t-shirts. D. excess supply of 10 t-shirts.