The nondiscriminating pure monopolist's demand curve:
A. is the industry demand curve.
B. shows a direct or positive relationship between price and quantity demanded.
C. tends to be inelastic at high prices and elastic at low prices.
D. is identical to its marginal revenue curve.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Describe the different possible profit outcomes for a perfectly competitive firm in the short run versus the long run. Explain why they occur
What will be an ideal response?
The diagram concerns supply adjustments to an increase in demand (D 1 to D 2 ) in the immediate market period, the short run, and the long run. In the immediate market period, the increase in demand will:
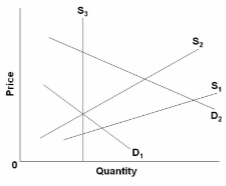
A. have no effect on either equilibrium price or quantity.
B. increase equilibrium price but not equilibrium quantity.
C. increase equilibrium quantity but not equilibrium price.
D. increase both equilibrium price and quantity.
A shift in the consumption function:
A. is based on the marginal propensity to consume. B. can be caused by a change in the price level. C. can be caused by a change in GDP. D. cannot be caused by a change in expectations.
The break-even price for a perfectly competitive firm is the price that is equal to
A. MC. B. MR C. AVC. D. ATC.