Determine the discriminant of the quadratic equation. Use the value of the discriminant to determine whether the quadratic equation has two rational solutions, two irrational solutions, one repeated real solution, or two complex solutions that are not real.x2 + 12x + 36 = 0
A. Two complex solutions that are not real
B. One repeated real solution
C. Two rational solutions
D. Two irrational solutions
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Identify the conic that the polar equation represents. Also, give the position of the directrix.r = 
A. ellipse, directrix parallel to the polar axis 1 below the pole B. ellipse, directrix perpendicular to the polar axis 1 left of the pole C. ellipse, directrix parallel to the polar axis 1 above the pole D. ellipse, directrix perpendicular to the polar axis 1 right of the pole
The sides in the pair of figures are proportional. Find the missing length(s).
A. x = 2, y = 4 B. x = 4, y = 6 C. x = 2, y = 3 D. x = 3, y = 4
The lengths of the sides of a triangle are given. Determine if the triangle is a right triangle. If it is, identify the hypotenuse.6, 8, 12
A. right triangle; 6 B. right triangle; 8 C. right triangle; 12 D. not a right triangle
For the pair of functions, find the quotient function or functional value indicated. Give any x-values that are not in the domain of the quotient function.Find 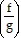 (x).f(x) = x2 - 2x - 8g(x) = x - 4
(x).f(x) = x2 - 2x - 8g(x) = x - 4
A. 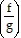 (x) = x + 2; 4
(x) = x + 2; 4
B. 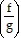 (x) = x + 2; -4
(x) = x + 2; -4
C. 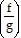 (x) = x + 4; 2
(x) = x + 4; 2
D. 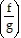 (x) = x + 2; 0
(x) = x + 2; 0