In 2.0 s, a particle moving with constant acceleration along the x axis goes from x = 10 m to x = 50 m. The velocity at the end of this time interval is 10 m/s. What is the acceleration of the particle?
a. +15 m/s2
b. +20 m/s2
c. ?20 m/s2
d. ?10 m/s2
e. ?15 m/s2
d
You might also like to view...
Determine the shape factor F1–4 for the geometrical configuration shown below.
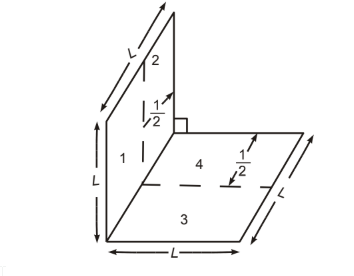
GIVEN
Geometrical configurations shown above
FIND
The shape factor F1–4
A gray opaque surface has an emissivity of 0.8 at 400ºF. Determine the radiosity if it is irradiated at 1000 Btu/hr?ft^2.
What will be an ideal response?
You are observing the wobble of a star caused by the orbit of a planet around that star. Which property of this system listed below most signi?cantly affects the period of that wobble?
A) the planet's orbital radius B) the planet's mass C) both the planet's orbital radius and its mass D) neither the planet's orbital radius nor its mass
Which part of the electromagnetic spectrum is the ozone-destruction problem related to?
A) visible B) X-rays C) radio D) infrared E) ultraviolet