For each of the following changes, what happens to the real interest rate and output in the very short run, before the price level has adjusted to restore general equilibrium?(a)Wealth declines.(b)Money supply declines.(c)The future marginal productivity of capital declines.(d)Expected inflation rises.(e)Future income rises.
What will be an ideal response?
| (a) | The IS curve shifts down and to the left, so r falls and Y falls. |
| (b) | The LM curve shifts up and to the left, so r rises and Y falls. |
| (c) | The IS curve shifts down and to the left, so r falls and Y falls. |
| (d) | The LM curve shifts down and to the right, so r falls and Y rises. |
| (e) | The IS curve shifts up and to the right, so r rises and Y rises. |
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below.________ inflation will eventually move the economy pictured in the diagram from short-run equilibrium at point ________ to long-run equilibrium at point ________, 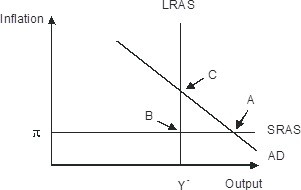
A. Rising; B; C B. Falling; A; C C. Falling; A; B D. Rising; A; C
The equilibrium real interest rate in Belgium will be
A) generally above the world real interest rate. B) generally below the world real interest rate. C) equal to the world real interest rate. D) determined by the equilibrium between desired domestic saving and desired domestic investment.
If the present value of an individual's savings account is $100,000, what is its future value in 5 years if the account earns an annual interest rate of 2 percent?
A) $112,125.40 B) $109,582.03 C) $110,250.00 D) $110,408.08
Which of the following activities would be considered tax avoidance?
a. increasing your level of charitable contributions in December b. selling illegal drugs on the street c. underestimating your income that is subject to taxation d. failure of a waitress to report all tips earned on the job e. buying a house and neglecting to deduct interest payments