As an object is lowered into a deep hole in the surface of the Earth, which of the following must be assumed in regard to its potential energy?
a. It increases.
b. It decreases.
c. It remains constant.
d. One cannot tell from the information given.
B
You might also like to view...
The strength of low-carbon steel used in automobile bodies is achieved by ______________forming.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
Potential of Point-Charges: Two +6.0-µC charges are placed at two of the vertices of an equilateral triangle having sides 2.0 m long. What is the electric potential at the third vertex, relative to infinity, due to these charges? (k = 1/4??0 = 9.0 × 109 N ? m2/C2)
A. 54 kV B. 108 V C. 0 V D. 90 kV E. 27 kV
What is the maximum length of a metal cable that can hang vertically supported from one end of the cable?
The Young's modulus of this metal is 2.10 × 1011 N/m2, its tensile strength (the maximum tensile stress it can support without breaking) is 7.40 × 108 N/m2, and its density is 7.60 × 103 kg/m3. A) 9.94 km B) 4.22 km C) 456 km D) 1.75 km E) 24.8 km
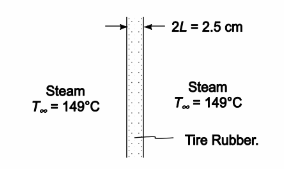
In the vulcanization of tires, the carcass is placed into a jig and steam at 149°C is admitted suddenly to both sides. If the tire thickness is 2.5 cm, the initial temperature is 21°C, the heat transfer coefficient between the tire and the steam is 150 W/(m2 K), and the specific heat of the rubber is 1650 J/(kg K), estimate the time required for the center of the rubber to reach 132°C.
GIVEN
• Tire suddenly exposed to steam on both sides
• Steam temperature (T?) = 149°C
• Tire thickness (2L) = 2.5 cm = 0.025 m
• Initial tire temperature (To) = 21°C
• The heat transfer coefficient (hc) = 150 W/(m2 K)
• The specific heat of the rubber (c) = 165 J/(kg K)
FIND
• The time required for the central layer to reach 132°C
ASSUMPTIONS
• Shape effects are negligible, tire can be treated as an infinite plate
SKETCH