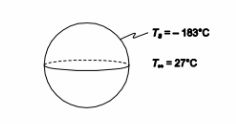
A cryogenic fluid is stored in a 0.3-m-diameter spherical container in still air. If the convection heat transfer coefficient between the outer surface of the container and the air is 6.8 W/(m2 K), the temperature of the air is 27°C and the temperature of the surface of the sphere is –183°C, determine the rate of heat transfer by convection.
GIVEN
• A sphere in still air
• Sphere diameter (D) = 0.3 m
• Convective heat transfer coefficient ch = 6.8 W/(m2K)
• Sphere surface temperature (Ts) = –183°C
• Ambient air temperature (T?) = 27°C
FIND
• Rate of heat transfer by convection (qc)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state heat flow
SKETCH
The rate of heat transfer by convection is given by
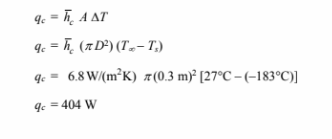
You might also like to view...
In the chrome plating of steel automotive parts, it is found that it is possible to have a high-quality coating with a current density of 0.4 A/cm 2 by heating the chromic acid solution to 65°C and using a chrome anode.

A car passes a dip in the road, going first down, then up. At the very bottom of the dip, when the car’s instantaneous velocity is passing through horizontal, how does the magnitude of the normal force on the car compare to the magnitude of the car’s weight?
A. 
B. 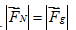
C. 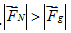
D. 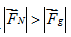
E. We do not have enough information to answer.
A 0.600-kg piece of metal X is heated to 100°C and placed in an aluminum can of mass 0.200-kg which contains 0.500 kg of water initially at 17.3°C
The final equilibrium temperature of the mixture is 20.2°C, what is the specific heat of metal X? The specific heats of water and aluminum are 4186 J/kg ? K (water) and 910 J/kg ? K (aluminum). A) 140 J/kg ? K B) 270 J/kg ? K C) 450 J/kg ? K D) 900 J/kg ? K
An object moves 10 m east in 30 s and then returns to its starting point taking an additional 70 s. If west is chosen as the positive direction, what is the average speed of the object?
a. 0.20 m/s c. 0.50 m/s b. –0.20 m/s d. 0 m/s