Find the inverse of the following one-to-one function.f(x) = 
A. f-1(x) = 
B. f-1(x) = 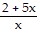
C. f-1(x) = 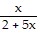
D. Not invertible
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
The function f is one-to-one. State the domain and the range of f and f-1. Write the domain and range in set-builder notation.f(x) = 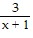
A. f(x): D =  , R =
, R = 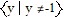 ;
;
f-1(x): D =  , R =
, R = 
B. f(x): D = {x|x ? -1}, R = {y ? 0};
f-1(x): D = {x|x ? 0}, R = {y|y ? -1}
C. f(x): D is all real numbers, R is all real numbers;
f-1(x): D is all real numbers, R is all real numbers
D. f(x): D is all real numbers, R =  ;
;
f-1(x): D = 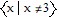 , R is all real numbers
, R is all real numbers
Solve the problem.A collection of dimes is arranged in a triangular array with 11 coins in the base row, 10 in the next, 9 in the next, and so forth with 1 dime in the last row. Find the value of the collection.
A. $13.20 B. $6.60 C. $3.30 D. $0.66
Write the fraction in decimal notation.
A. 2.85 B. 2.24 C. 2.275 D. 2.28
Two sides and an angle are given. Determine whether the given information results in one triangle, two triangles, or no triangle at all. Solve any triangle(s) that results.a = 3, b = 2, B = 20°
A. one triangle A = 149.13°, C = 10.87°, c = 1.1 B. two triangles A1 = 30.87°, C1 = 129.13°, c1 = 4.54 or A2 = 149.13°, C2 = 10.87°, c2 = 1.1 C. one triangle A = 30.87°, C = 129.13°, c = 4.54 D. no triangle