Refer to the diagram in which T is tax revenues and G is government expenditures. All figures are in billions. In this economy:
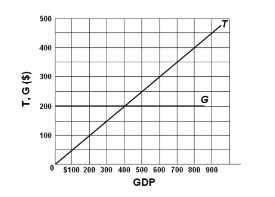
A. tax revenues and government spending both vary directly with GDP.
B. tax revenues vary directly with GDP, but government spending is independent of GDP.
C. tax revenues and government spending both vary inversely with GDP.
D. government spending varies directly with GDP, but tax revenues are independent of GDP.
B. tax revenues vary directly with GDP, but government spending is independent of GDP.
You might also like to view...
Describe some of the benefits and costs associated with the emergence of large cities in developing countries
What will be an ideal response?
The AA schedule shows
A) Interest rate and output pairs at which the foreign exchange market and the domestic money market are in equilibrium. B) Exchange rate and output pairs at which the foreign exchange market and the domestic money market are in equilibrium. C) Interest rate and output pairs at which only the foreign exchange market is in equilibrium. D) Exchange rate and output pairs at which only the foreign exchange market is in equilibrium. E) Exchange rate and output pairs at which only the domestic money market are in equilibrium.
One practical implication of a kinked market supply curve is that:
A) producer surplus is not defined at the kink point. B) the MC = MR rule does not hold at the kink point. C) the market supply elasticity for a price increase may be different than the market supply elasticity for a price decrease at the kink point. D) All of the above are true.
Which of the following is correct?
A. Both conservative economists and Keynesians believe the crowding-out effect is small. B. Both conservative economists and Keynesians believe the crowding-out effect is large. C. Conservative economists believe the crowding-out effect is small, while Keynesians believe it is large. D. Conservative economists believe the crowding-out effect is large, while Keynesians believe it is small.