Consider a large open economy that has a positive current account balance. (a) Suppose the domestic government increases the tax rate on firm revenues
Draw a diagram to explain the effects on the world real interest rate, saving in each country, investment in each country, and the current account balance in each country in equilibrium. Explain your work. (b) In addition to the tax increase in part (a), suppose now that the foreign government increases lump-sum taxes on individuals. Draw a new diagram to incorporate the overall effects of both tax changes and explain the effects (from the initial equilibrium with neither tax change) on the world real interest rate, saving in each country, investment in each country, and the current account balance in both countries. Explain your work.
(a) The increased tax rate on firm revenues increases the tax-adjusted user cost of capital, thus reducing desired investment in the domestic country. To restore equilibrium, the world real interest rate must decline. In equilibrium, both saving and investment in the domestic country are lower; while in the foreign country, saving is lower but investment is higher. The lower saving and higher investment in the foreign country mean that the current account balance is lower in the foreign country. Because the sum of the two countries' current account balances must be zero, the lower foreign current account balance means that the domestic country's current account balance must be higher.
(b) If Ricardian Equivalence holds, then all the answers are the same as in part (a). If Ricardian Equivalence does not hold, then the foreign tax increase would increase desired foreign saving and reduce the world real interest rate even more than in part (a). Compared with the initial equilibrium, both domestic saving and investment are lower and foreign investment is higher. The effect on foreign saving is ambiguous, as the effect of the tax change in part (a) reduces it but the tax change in part (b) increases it. As a result, the current account balance in the foreign country is ambiguous, as is the current account balance in the domestic country.
You might also like to view...
Refer to Table 29-3. Given the following exchange rates in the above table, what are the exchange rates stated as U.S. dollars per Danish krone and U.S. dollars per EU euro respectively?
A) 2.00 dollars per krone and 7.14 dollars per euro B) 0.02 dollars per krone and 0.70 dollars per euro C) 0.20 dollars per krone and 1.43 dollars per euro D) 0.05 dollars per krone and 1.30 dollars per euro
The wage premium for the average college graduate (vs. the average high school graduate) has gone down significantly in recent years
a. True b. False
The idea of compensating differences is used:
A. by inclusive unions as an argument in bargaining for wage rate increases. B. to justify the application of minimum wages to low-wage labor markets. C. to explain the divergence between wage rates and marginal resource cost. D. to explain wage rate differences based on differing nonmonetary aspects of jobs.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 27.3 below to answer the question(s) that follow.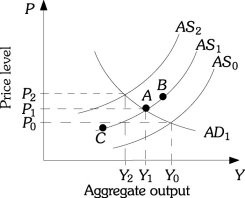 Figure 27.3Refer to Figure 27.3. Assume the economy is at Point A. Higher oil prices shift the aggregate supply curve to AS2. If the government decides to counter the effects of higher oil prices by increasing net taxes, then the price level will be ________ than P2 and output will be ________ than Y2.
Figure 27.3Refer to Figure 27.3. Assume the economy is at Point A. Higher oil prices shift the aggregate supply curve to AS2. If the government decides to counter the effects of higher oil prices by increasing net taxes, then the price level will be ________ than P2 and output will be ________ than Y2.
A. less; less B. less; greater C. greater; less D. greater; greater