Which of the following types of goods would most likely be classified as a government-inhibited good?
A) heroin
B) marijuana
C) tobacco
D) All of the above are correct.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
With ________ finance, borrowers obtain funds from lenders by selling them securities in the financial markets
A) active B) determined C) indirect D) direct
Labor demand depends on the interest rate because
A) household savings depend on the interest rate. B) firms discount future profits. C) of Ricardian equivalence. D) Labor demand actually does not depend on the interest rate.
Assume that the central bank lowers the discount to increase the nation's monetary base. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a fixed exchange rate system, what happens to the quantity of real loanable funds per time period and net nonreserve international borrowing/lending balancein the context of the Three-Sector-Model? State your answer after the macroeconomic
system returns to complete equilibrium. a. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period remains the same and net nonreserve international borrowing/lending balance becomes more negative (or less positive). b. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period rises and net nonreserve international borrowing/lending balance becomes more negative (or less positive). c. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period falls and net nonreserve international borrowing/lending balance becomes more positive (or less negative). d. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period and net nonreserve international borrowing/lending balanceremain the same. e. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables.
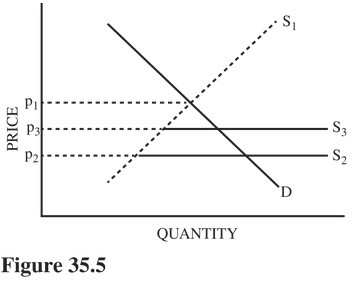 Refer to Figure 35.5. If S1 represents the U.S. domestic supply of a good and S2 represents supply in the United States under conditions of free trade, what does S3 most likely represent?
Refer to Figure 35.5. If S1 represents the U.S. domestic supply of a good and S2 represents supply in the United States under conditions of free trade, what does S3 most likely represent?
A. The result of a foreign country dumping this good on the U.S. market. B. U.S. supply under quota-restricted trade. C. U.S. supply under tariff-restricted trade. D. Production possibilities under conditions of free trade.