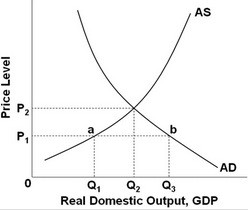
 Refer to the above graph. At price level P2:
Refer to the above graph. At price level P2:
A. the quantity of output supplied is constant.
B. the quantity of output supplied is less than the quantity of output demanded.
C. the quantity of output supplied is greater than the quantity of output demanded.
D. the quantity of output supplied is equal to the quantity of output demanded.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
The deadweight loss caused by a monopoly is the area:
a. between the demand curve and the marginal cost curve and between the profit-maximizing quantity and the efficiency quantity. b. between the demand curve and the marginal revenue curve and between the profit-maximizing quantity and the efficiency quantity. c. under the marginal revenue curve and between the profit-maximizing quantity and the efficiency quantity. d. under the marginal cost curve and the marginal revenue curve and between the profit-maximizing quantity and the efficiency quantity.
Suppose buyers of fountain drinks are required to send $0.50 to the government for every fountain drink they buy. Further, suppose this tax causes the effective price received by sellers of fountain drinks to fall by $0.20 per drink. Which of the following statements is correct?
a. This tax causes the demand curve for fountain drinks to shift downward by $0.50 at each quantity. b. The price paid by buyers is $0.30 per drink more than it was before the tax. c. Forty percent of the burden of the tax falls on sellers. d. All of the above are correct.
Suppose that the equilibrium price of apples decreases and the equilibrium quantity of apples increases. This is best explained by:
A. an increase in the demand for apples. B. an increase in the supply of apples. C. a decrease in the demand for apples. D. a decrease in the supply of apples.
Comparative advantage refers to a country's:
A. Ability to produce a specific good with fewer resources than another country. B. Monopoly power in the world market for a specific good. C. Ability to sell a specific good for a higher price than another country. D. Ability to produce a specific good at a lower opportunity cost than another country.