Which of the following methods used to determine the mass of a cluster of galaxies does not depend on Newton's law of gravity?
A) measuring the orbital velocities of galaxies in the cluster
B) measuring the temperature of x-ray gas in the intracluster medium
C) measuring the amount of distortion caused by gravitational lensing
C) measuring the amount of distortion caused by gravitational lensing
You might also like to view...
A 200-volt battery is connected to a 0.50-microfarad parallel-plate, air-filled capacitor. Now the battery is disconnected, with care taken not to discharge the plates. Some Pyrex glass is then inserted between the plates, completely filling up the space. What is the final potential difference between the plates? (The dielectric constant for Pyrex is ? = 5.6.)
In a steady flow in a long pipe, such as the Alaska oil pipe line, the Eulerian description of the velocity field would express the velocity V in the pipe as:
(A) V(t) (B) V(r) (C) V(r, t) (D) V(r, z)
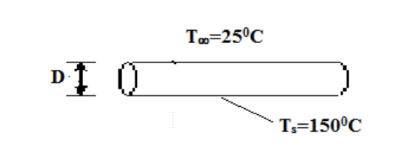
A long, heated, cylindrical steel rod is removed from a heat treatment furnace and has to be cooled to complete the process. If the surface temperature of the rod is at 150°C and the cooling fluid temperature is maintained at 25°C, what is the minimum diameter of the rod to produce turbulent natural convection heat transfer if it is held in a horizontal position in (a) air and (b) water? Also, determine the initial heat transfer rate by natural convection from a 10-cm diameter rod in each of the two fluids.
GIVEN
• Long heated cylindrical steel rod, cooled by natural convection.
• Surface temperature of rod (Ts=1500C
• Fluid temperature (T?) = 250C
FIND
(a) Minimum diameter of rod to produce turbulent natural convection in (i) Air (ii) water
(b) Initial heat transfer rate by natural convection from 10 cm diameter rod in each fluids.
ASSUMPTIONS
• Radiation is negligible
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for dry air at the mean temperature of 87.5°C
Thermal expansion coefficient (?) = 0.00277 1/K
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0298 W/(m K)
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 22.55 × 10–6 m2/s
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71
for water at the mean temperature of 87.5°C
Thermal expansion coefficient (?) = 0.000678 1/K
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.6765 W/(m K)
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 0.33 × 10–6 m2/s
Prandtl number (Pr) = 67.8
Almost all of our atmospheric gases lie in the
A) ozone layer. B) mesosphere. C) ionosphere. D) troposphere. E) stratosphere.