Contrast the actions the central bank of a country would take to increase the quantity of money in an economy with the actions it would take to produce the opposite effect
A central bank that wants to increase the money supply in the economy can buy bonds in an open market operation, reduce the reserve requirement, lower the discount rate, or engage in quantitative easing. An open market purchase of bonds will encourage banks to make loans instead of holding its assets in the form of government bonds. As these loans are deposited into checking accounts, the money supply will expand because checking accounts are part of M1 . If banks are allowed to hold a smaller amount in reserves, then they will have a greater amount of money available to lend out. If the central bank lowers the discount rate that it charges to banks, banks will be willing to lend more aggressively, which will increase the money supply. The central bank can purchase bank debt, mortgage-backed securities, and Treasury notes as a part of quantitative easing to expand the quantity of money in the economy.
Conversely, a central bank that wants to reduce the money supply in the economy can sell bonds in an open market operation, raise the reserve requirement, raise the discount rate, or reverse its past practices of quantitative easing. An open market sale of government bonds will reduce the amount of loans given by banks, leading to a reduction in money supply. If banks are required to hold a greater amount in reserves, they will have less money available to lend out. If the central bank raises the discount rate, then banks will hold a higher level of reserves and reduce the amount of lending, thus reducing the money supply in the economy as a whole.
You might also like to view...
The lower the level of income in a country, the
A) less income elastic is the demand for food. B) more income elastic is the demand for food. C) more negative the income elasticity of the demand for food. D) Both answers A and C are correct. E) None of the above is correct.
An individual's permanent income is
A) constant over time. B) the same as his current income. C) unaffected by tax changes. D) equal to his expected average income.
How might command-and-control regulations be described?
a. Highly incentivized b. Easy to implement c. Inflexible d. Flexible
Which point shows where the United States economy was temporarily operating during World War II, when we had reduced the unemployment rate to about two percent?
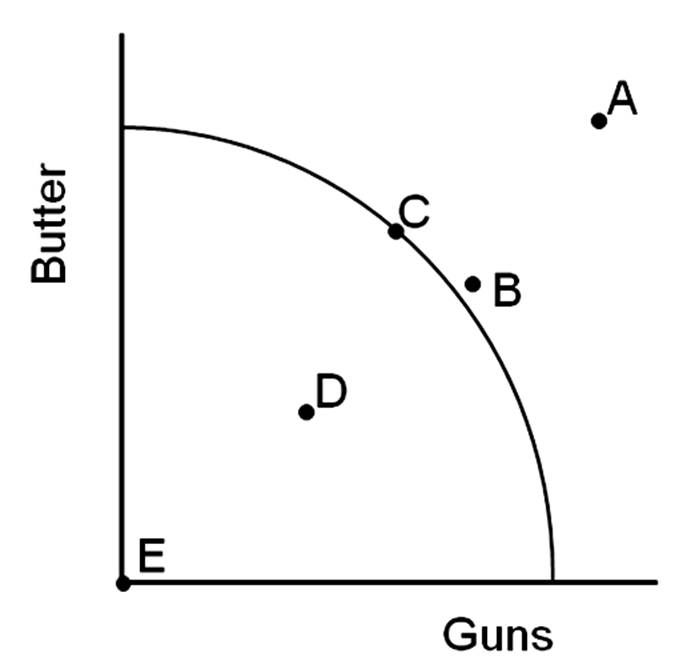
A. Point A
B. Point B
C. Point C
D. Point D