What are the six main horizons found in soils? Briefly describe each
What will be an ideal response?
O, A, E, B, C, and R. (Note, the text lists four "main" horizons, then describes the six horizons, which other texts also call master horizons).
The O horizon is high in organic matter content, derived from litter that is transformed into humus. It is 20-30% organic matter and retains water and nutrients.
The A horizon, often called topsoil, contains humus and clay particles. This horizon provides an essential chemical link between soil nutrients and plants.
The E horizon is a zone of eluviation, where various materials are leached to the horizon below. It is composed mainly of coarse sand, silt, and leaching resistant minerals.
The B horizon is a zone of illuviation where the translocated minerals and other matter leached from the E horizon accumulate.
The C horizon is a zone of regolith, i.e. weathered bedrock and parent material.
The R horizon consists of unconsolidated rock material or consolidated bedrock.
You might also like to view...
The price consumers are willing to pay for a resource that may be limited depends on ________
A) how much they can afford at a time the resource is limited B) their access to the resource in their community C) their perceived need for the resource D) how much of the resource is remaining to purchase E) their ability to pay more than someone else
What method of hunting do Arctic foxes use?
What will be an ideal response?
Which of the numbered features is a pyroclastic column?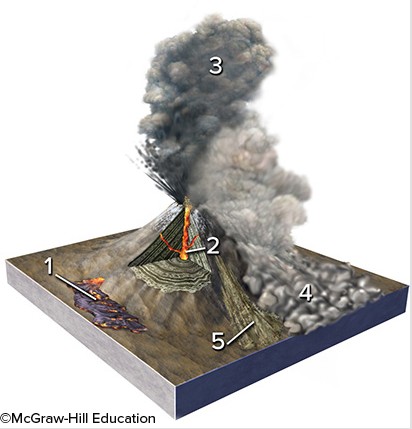
A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 E. 5
What are some of the economic challenges that Quebec has faced over the years in its primary sector as compared to its secondary sector of production?
What will be an ideal response?