In countries with low levels of income:
a. the opportunity cost of an education is higher than in high-income countries.
b. illiteracy rates are higher than in high-income countries
c. economies are primarily agricultural-based.
d. all of the above tend to be true.
d
You might also like to view...
As a firm increases its output in the short run, average fixed cost
a. rises steadily b. falls and then rises c. falls steadily d. rises and then falls e. remains unchanged
From a union's perspective, the optimal level of employment is determined by the intersection of the
A. Labor demand curve and the marginal wage curve. B. Labor demand curve and the marginal factor cost curve. C. Labor demand curve and the labor supply curve. D. Marginal wage curve and the labor supply curve.
A firm with a demand curve P = 10 - Q is a perfect price discriminating monopolist with zero marginal costs and fixed costs of 12. Consider the following two statements comparing the price discriminating case with a single price monopolist. 1) In this case consumers are better off as a group because more of the product is produced. 2) Producers are better off because they have higher profits. Which of the following comments about these statements is true? 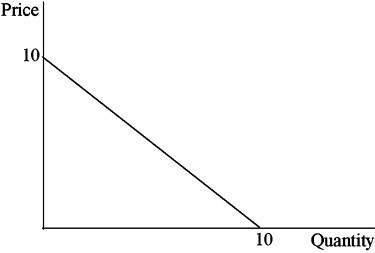
A. Only the second statement is true. B. Both statements are true. C. Both statements are false. D. Only the first statement is true.
The marginal propensity to consume is difficult to estimate because
a) it depends on expectations of future income b) it depends on perceptions regarding the permanence of changes in income c) it depends on credit and borrowing constraints d) it declines as uncertainty increases e) all of the above