Describe the two example-selection guidelines to consider when teaching students to convert a fraction to a percent. Explain why these example-selection guidelines are important
What will be an ideal response?
Two example-selection guidelines are critical for teaching students to convert a fraction to a decimal. First, proper and improper fractions should be included so that students can see that the strategy also applies to percentages greater than 100% ![]() The second example selection guideline relates to the need to round answers. Initially, problems should be limited to fractions that do not require rounding off to compute the percent. Problems that must be rounded off require an extra step and should not be introduced for several weeks. The fractions
The second example selection guideline relates to the need to round answers. Initially, problems should be limited to fractions that do not require rounding off to compute the percent. Problems that must be rounded off require an extra step and should not be introduced for several weeks. The fractions ![]() are examples of fractions that do not require rounding off. Later, fractions such as
are examples of fractions that do not require rounding off. Later, fractions such as 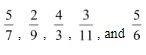 that do require rounding off may be included.
that do require rounding off may be included.
You might also like to view...
As a general rule, the larger the degrees of freedom for a chi-square test, ______.
A. the smaller the critical value will be B. the larger the critical value will be C. the smaller the level of significance will be D. the larger the level of significance will
Scheduling in the primary grades should:
a. Include large blocks of time to accommodate various kinds of project work. b. Include language arts at the beginning of the day when children are fresh and better able to concentrate. c. Accommodate young children's short attention spans by frequent changes in activity. d. Both a and b
Which of the following components of temperament are most relevant to the development of autonomy?
a. Sensitivity, adaptability and activity level b. Adaptability, persistence and approach c. Reactivity, approach and activity level d. Approach, adaptability and reactivity
Explain differentiated instruction. Discuss its meaning, its purpose, and ways to implement it in your classroom
What will be an ideal response?