Imagine you are plunging into the Sun, starting from Earth. Briefly describe what you will experience on your journey
What will be an ideal response?
First you will experience the light of the Sun and the pressure of particles from the solar wind. As you approach within a few radii of the Sun, you will enter the corona, an extremely hot, but tenuous layer of gas. The next layer you encounter will be the chromosphere, a hot layer of gas just above the visible surface of the Sun. As you plunge through the Sun's "surface", the photosphere, the temperature of the gas will be about 5,800 K, which is cooler than the outer layers. You will also see the slightly cooler regions of sunspots and the granulation on the surface caused by the convection underneath. You will then enter this convective layer, feeling regions of hot plasma rising upward to meet you and seeing cooler gas descending from the surface. After passing through this layer, you will reach the radiation zone, where photons are engaged in a random dance as they are continuously absorbed and reemitted by the hot gas there. You will then reach the source of these photons, the core of the Sun, which is actively involved in nuclear fusion, converting hydrogen into helium and releasing multitudes of photons and neutrinos.
You might also like to view...
Answer the following statement(s) true (T) or false (F)
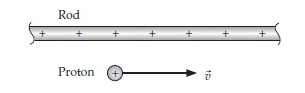
1. The rod creates an electric field in that frame.
2. The rod creates a magnetic field in that frame.
3. The proton feels an electric force in that frame.
4. The proton feels a magnetic force in that frame. Now consider a frame moving along with the proton.
5. The rod creates an electric field in that frame
Several of the tributary canyons of the Valles Marineris on Mars are thought to be formed:
A. when water coming from the volcanoes started flowing through the planet. B. from impacts with irregularly shaped comets and asteroids. C. from a chemical reaction between iron oxide and water. D. when strong wind currents along the equatorial region started blowing out sand. E. when ground water, escaping from opening cracks, flowed and cut a channel through the surface beneath.
A 1000-kg whale swims horizontally to the right at a speed of 6.0 m/s. It suddenly collides directly with a stationary seal of mass 200 kg. The seal grabs onto the whale and holds fast
What is the speed of these two sea creatures just after their collision? You can neglect any drag effects of the water during the collision. A) 0.00 m/s B) 3.0 m/s C) 4.0 m/s D) 5.0 m/s E) 6.0 m/s
Copper-66 decays to zinc-66 when it emits a(n) ______________
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word