Many firms use odd pricing—charging prices such as $.99 instead of $1.00 and $9.99 instead of $10.00
One reason for this pricing strategy is that consumers will somehow believe that the difference in price appears to be greater than it actually is. Researchers conducted consumer surveys to determine whether this is actually the case. What was the result of these surveys?
A) The survey results were inconclusive because most consumers gave unreliable responses to the survey questions.
B) Although the results were not conclusive, there is some evidence that odd pricing makes economic sense.
C) The surveys found indifference regarding this strategy among most consumers, but hostility among other consumers. The latter group resented what they viewed as an attempt to fool them into buying products with odd prices. Researchers concluded that odd pricing is counterproductive.
D) The surveys found that small differences in price cause small differences in quantity demanded. There is no evidence that odd pricing makes economic sense.
B
You might also like to view...
What name is given to the plant and equipment used by firms in production?
A. Production function B. Physical capital C. Productivity D. Aggregate production function
In order to be successful in a market economy, entrepreneurs must
What will be an ideal response?
Which of the following is one of the main causes of the fiscal crisis in Greece?
A. Greece experienced high birth rate and low death rate between 2000 and 2010. B. Greece's prime minister did not have the desire to tackle difficult structural issues. C. Greece did not have a strong labor force to support production. D. Greece had a high national debt and high deficits prior to the crisis.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 9.5 below to answer the question that follows. 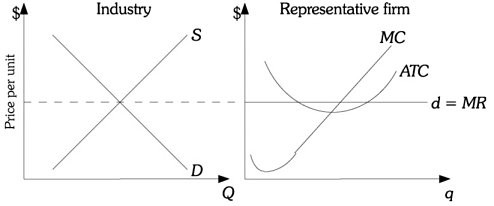 Figure 9.5Refer to Figure 9.5. Based on the figures, supply will ________ in the long run and profits should ________.
Figure 9.5Refer to Figure 9.5. Based on the figures, supply will ________ in the long run and profits should ________.
A. increase; decline B. decrease; increase C. increase; increase D. decrease; decline