The above figure shows the demand and cost curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the long run. The maximum economic profit this firm can make equal equals
A) $0.
B) $80.
C) $120.
D) $160.
A
You might also like to view...
Why does rent-seeking behavior lead to deadweight loss?
Suppose an excise tax is imposed on luxury boats and yachts. Economists argue that such a tax
a. is sure to be vertically equitable, since buyers of luxury boats and yachts are wealthy. b. entails no deadweight loss as long as buyers of boats and yachts can easily substitute one luxury good for another. c. violates the benefits principle of taxation. d. may burden workers in the luxury-boat-and-yacht industry more than it burdens the buyers of luxury boats and yachts.
When the housing bubble popped, the effect of the negative demand side shock and the negative supply side shock were the same on:
A. output, causing it to definitely decrease. B. prices, causing them to definitely rise. C. output, causing it to definitely increase. D. prices, causing them to definitely fall.
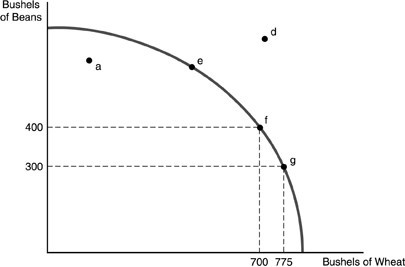 Refer to the above figure. Between points f and g, the opportunity cost of producing 75 more bushels of wheat is
Refer to the above figure. Between points f and g, the opportunity cost of producing 75 more bushels of wheat is
A. 4 bushels of beans. B. 100 bushels of beans. C. 1 bushel of beans. D. 25 bushels of beans.