Make a case for income inequality.
What will be an ideal response?
First, by rewarding people for their productivity by paying them wages equal to their MRPs, people have the incentive to work and improve their skills. Since MRPs vary, people must receive different wage rates, even though this will lead to income inequality. Second, because the rich can afford to save a higher percentage of their income than can the poor, they tend to do the economy's investing, thus generating economic growth that benefits everyone.
You might also like to view...
Refer to Figure 4-18. What is the size of the unit tax?
A) $8 B) $5 C) $3 D) cannot be determined from the figure
Menu costs ________
A) are the cost a firm bears when it changes its prices B) are one source of price stickiness because changing prices involves many hidden costs C) are one source of price stickiness because firms may not want to change their "menus" too often and risk alienating customers D) all of the above E) none of the above
Refer to the table below. Busy Betty sells her cakes for $20 each and her constant marginal cost to produce each cake is $12, which is equal to her (constant) average total cost. What is her expected marginal benefit from holding the 21st cake in inventory?
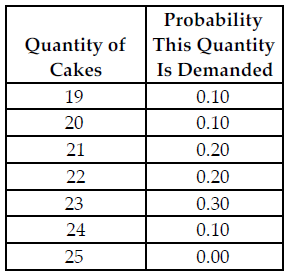
The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.
A) $6.10
B) $7.20
C) $6.40
D) $8.00
Which of the following statements is true?
a. Marginal revenue product is the extra revenue generated to the firm from the production of one more unit of output. b. Marginal factor cost is the extra cost to a firm of employing one more unit of a factor of production. c. The demand curve for a perfectly competitive employer is horizontal at the market wage rate. d. The supply curve of labor is upward sloping because of the law of diminishing marginal productivity.