The marginal propensity to save is
A) real consumption/real disposable income.
B) change in real saving/change in real disposable income.
C) change in real consumption/change in real disposable income.
D) real saving/real disposable income.
B
You might also like to view...
How does an increase in the budget deficit affect the demand for dollars and the supply of dollars on the foreign exchange market?
A) The demand for dollars rises, and the supply of dollars rises. B) The demand for dollars rises, and the supply of dollars falls. C) The demand for dollars falls, and the supply of dollars rises. D) The demand for dollars falls, and the supply of dollars falls.
Refer to the table below. If the profit for each unit of paper product is $2 and the profit for each unit of lumber is $5, what is the marginal benefit for each unit of lumber produced?
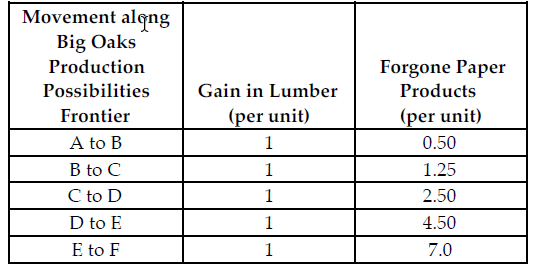
Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amount of paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable proportions. The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.
A) $3
B) $7
C) $2
D) $5
According to Keynesians, an increase in the money supply will have its greatest impact on GDP when the aggregate demand curve intersects:
a. the vertical portion of the aggregate supply curve. b. the upward sloping portion of the aggregate supply curve. c. the horizontal portion of the aggregate supply curve. d. either the upward sloping or the vertical portions of the aggregate supply curve. e. either the horizontal or vertical portions of the aggregate supply curve.
Suppose the U.S. removes an import quota on steel. U.S. exports
a. increase, the real exchange rate of the U.S. dollar appreciates, and U.S. net capital outflow increases. b. increase, the real exchange rate of the U.S. dollar depreciates, and U.S. net capital outflow is unchanged. c. decrease, the real exchange rate of the U.S. dollar appreciates, and U.S. net capital outflow is unchanged. d. decrease, the real exchange rate of the U.S. dollar depreciates, and U.S. net capital outflow decreases.