Referring to Figure 4.1, the increase in output from point A to B and from point B to C happens because 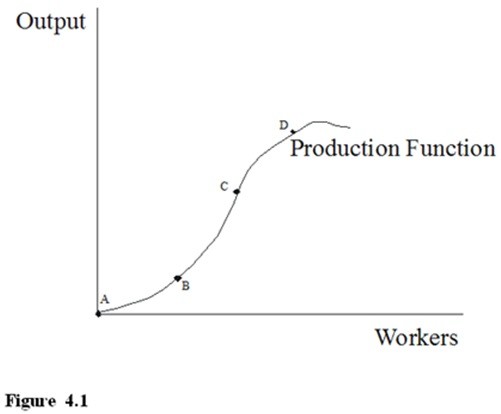
A. eventually workers are up against the fact that there are fixed inputs and more workers do not add as much.
B. a small number of workers cannot take as good advantage of the division of labor as a larger number.
C. better workers are usually hired after the earlier ones.
D. more workers will produce more.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Starting from long-run equilibrium, a large decrease in government purchases will result in a(n) ________ gap in the short-run and ________ inflation and ________ output in the long-run.
A. expansionary; lower; potential B. expansionary; higher; potential C. recessionary; lower; potential D. recessionary; lower; lower
Many economists argue that an incentive to save is
A) strengthening the property rights that savers have to the physical capital they purchase. B) greater government regulation of the banking and securities industries. C) a tax on consumption rather than on income. D) a tax on income rather than a tax on consumption. E) high income tax rates.
An increase in short-run aggregate supply shifts the curve ______.

a. from SRAS2 to SRAS1
b. from LRAS2 to SRAS1
c. from SRAS1 to LRAS1
d. from SRAS1 to SRAS2
The behavior of regulators when trying to win approval for their actions from their entire constituency is best described by the
A. share-the-gains, share-the-pains hypothesis. B. marginal benefit pricing hypothesis. C. capture hypothesis. D. law of increasing social well-being.