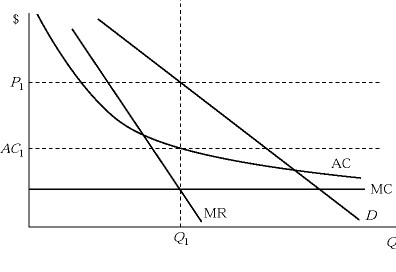
 Figure 11.1Figure 11.1 depicts demand and costs for a monopolistically competitive firm. At the profit maximizing output level:
Figure 11.1Figure 11.1 depicts demand and costs for a monopolistically competitive firm. At the profit maximizing output level:
A. this firm is earning economic profits equal to zero.
B. this firm is earning economic profits equal to Q1(P1 - AC1).
C. this firm is earning economic profits equal to P1(Q1 - AC1).
D. this firm is in long-run equilibrium.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
An industry is made up of 8 firms with the following percent market shares: 29, 20, 11, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6. What is the Herfindahl-Hirschman index in this industry?
A) 70 B) 100 C) 1462 D) 1692
Use the above table. Assuming constant opportunity costs, if countries Alpha and Beta specialize based on comparative advantage, then
A) Alpha should specialize in knives and Beta should specialize in forks. B) Alpha should specialize in forks and Beta should specialize in knives. C) Alpha should specialize in producing both items. D) Beta should produce both items.
If an individual has a constant MRS of shoes for sneakers of 3/4 (that is, he or she is always willing to give up 3 pairs of sneakers to get 4 pairs of shoes) then, if sneakers and shoes are equally costly, he or she will
a. buy only sneakers. b. buy only shoes. c. spend his or her income equally on sneakers and shoes. d. wear sneakers only 3/4 of the time.
Which of the following statements contradicts an upward-sloping market-supply curve?`
a. All people have backward-bending individual supply curves. b. Leisure is more enjoyable than work. c. The elasticity of labor supply is larger than the elasticity of labor demand. d. To work more means to enjoy less leisure. e. The opportunity cost of leisure decreases with an increase in wage rate.