This graph depicts the demand for a normal good.
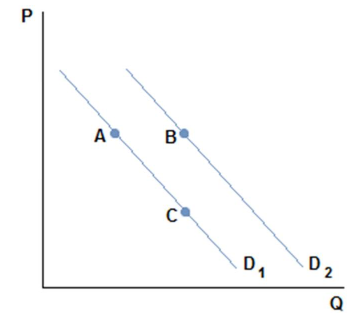
Suppose Johnny was consuming a normal good at point A in the figure shown, but has just received a raise at work. Johnny's demand may:
A. be unaffected.
B. increase to point B.
C. increase to point C.
D. drop to zero.
B. increase to point B.
You might also like to view...
Use the intertemporal budget constraint — equation (2 ) — to explain how an increase in the real interest rate causes two distinct effects, an income effect and a substitution effect,
and how those effects differ depending on whether the consumer is a saver or a borrower.
The index that is not based on a fixed market basket of goods and services is the
A) CPI. B) PPI. C) Wholesale Price Index. D) GDP Price Deflator.
Which would be least likely to cause the production possibilities curve to shift to the right?
a. An increase in the labor force. b. Improved methods of production. c. An increase in the education and training of the labor force. d. A decrease in unemployment.
Why is free trade considered helpful to businesses?
a. It gives consumers more choices. b. It increases competition. c. It opens up wider markets. d. It keeps consumer prices down.