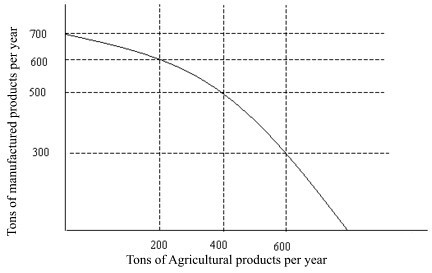
 The production possibilities curve in Figure 2.1 illustrates the notion of:
The production possibilities curve in Figure 2.1 illustrates the notion of:
A. increased factory goods production.
B. increased agricultural production.
C. diminishing resources.
D. opportunity cost.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
A negative cross elasticity indicates that two goods are complements.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Ricardian equivalence argues that when the government
A) increases taxes and raises its deficit, consumers anticipate that they will face higher taxes later to pay for the resulting government debt, thus people will raise their own private saving to offset the fall in government saving. B) cuts taxes and decreases its deficit, consumers anticipate that they will face higher taxes later to pay for the resulting government debt, thus people will raise their own private saving to offset the fall in government saving. C) cuts taxes and raises its surplus, consumers anticipate that they will face higher taxes later to pay for the resulting government debt, thus people will raise their own private saving to offset the fall in government saving. D) cuts taxes and raises its deficit, consumers anticipate that they will face lower taxes later to pay for the resulting government debt, thus people will raise their own private saving to offset the fall in government saving. E) cuts taxes and raises its deficit, consumers anticipate that they will face higher taxes later to pay for the resulting government debt, thus people will raise their own private saving to offset the fall in government saving.
To practice second-degree price discrimination
A) different markets must be able to communicate with each other. B) different markets must have the same number of customers. C) similar markets must have similar elasticities. D) different markets must have different elasticities.
An LDC can experience economic development at virtually zero opportunity cost by
a. establishing a comprehensive banking system b. taxing its citizens at a higher rate c. bringing in foreign direct investment d. increasing its population growth rate e. giving up consumer goods to acquire capital goods