If total cost at quantity = 0 is $100 and total cost at quantity = 10 is $500, then average variable cost at quantity = 10 is _____
a. $500
b. $400
c. $50
d. $40
e. $10
Answer: d. $40
You might also like to view...
Suppose there are three houses in a neighborhood. The residents are considering installing street lights and are trying to determine how many lights need to be installed
Each resident's willingness to pay for street lights is given in the table below. Number of Street Lights House 1 House 2 House 3 1 $300 $400 $200 2 $280 $360 $160 3 $240 $300 $120 4 $180 $220 $100 5 $80 $100 $10 If the cost of installing one light is $500, how many lights will be installed? A) 1 B) 2 C) 4 D) 5
A feature of debt markets in emerging-market countries is that debt contracts are typically
A) very short term. B) long term. C) intermediate term. D) perpetual.
A freeze in Florida's orange growing regions will:
A) result in a sharp increase in the price of oranges in the short run because demand and supply are highly inelastic. B) result in a sharp increase in the price of oranges in the short run because demand and supply are highly elastic. C) result in a sharp decrease in the price of oranges in the short run because demand is highly inelastic and supply is highly elastic. D) result in little change in the price of oranges in the short run because supply is infinitely elastic.
Assume Claudia's budget constraint is demonstrated by line A in the graph shown. Which of the following would cause Claudia's budget constraint to shift to line C?
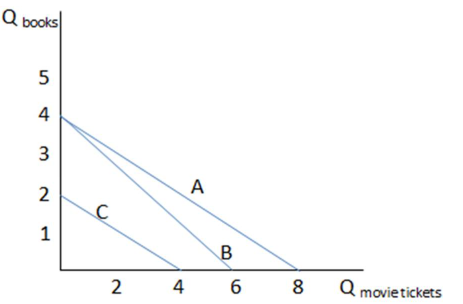
A. The price of books dropped.
B. The price of movie tickets dropped.
C. Claudia's preferences for these two goods decreased.
D. Claudia’s income decreased.