Which pattern of diploid and haploid phases reflects the life cycles of some fungi and algae, but NOT the life cycles of plants or animals?
a. two haploid generations followed by a diploid generation
b. one haploid generation followed by two diploid generations
c. a life cycle that limits the diploid state to a single cell produced by fertilization
d. alternation between haploid and diploid generations
Answer: c. a life cycle that limits the diploid state to a single cell produced by fertilization
You might also like to view...
Muscle samples are taken from two groups of men. One group performs regular intense aerobic exercise. The second group is sedentary and does not exercise. When you compare their muscle samples at the microscopic level, you expect to find that the exercising men show increases in
A. Golgi apparatus. B. capillary density. C. smooth endoplasmic reticulum. D. mitochondria. E. mitochondria and capillary density.
Why are waves of calcium that enter cells and are propagated through the cytoplasmic compartment, as happens within the first minute or so after fertilization, generally transient?
a) The ions are changed to calcium salts as soon as they enter the cell. b) The Ca2+ ions are rapidly pumped out of the cytosol and back into the ER and/or the extracellular space. c) The ions are destroyed as soon as they enter the cell. d) Option D: The Ca2+ ions are rapidly pumped out of the cytosol and back into the nucleus.
Animal cells are permeable to water and urea but NOT to sucrose. Initially, the inside of a cell contains 1 M sucrose and 1 M urea and the outside 2 M sucrose and 1 M urea. After the system reaches equilibrium, what changes are observed?
A. The molarity of sucrose would be similar inside and outside the cell and water would move out of the cell causing the cell to shrivel. B. The molarity of urea would be higher outside than inside the cell. C. Water would move out of the cell causing the cell to shrivel. D. The molarity of urea would be higher outside the cell and the molarity of sucrose would be similar inside and outside the cell. E. The molarity of sucrose would be similar inside and outside the cell.
Figure 17.2 In Figure 17.2, What portion will typically attach to a host cell? e a and d a and c b b and c
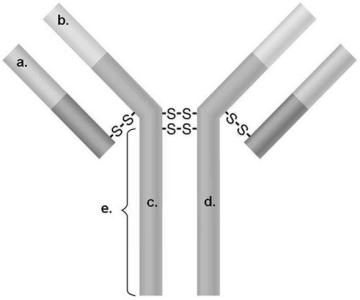
A) a and c
B) b
C) b and c
D) a and d
E) e