Many cells of the immune system have receptors that detect peptidoglycans and lipopolysaccharides. How do pathogenic bacteria avoid detection?
A. Pathogenic bacteria lack cell walls.
B. Pathogens often encase themselves in a gelatinous capsule.
C. Peptidoglycans are absent from pathogenic bacteria.
D. Disease is only possible if the immune system has been compromised by some other event.
Clarify Question
· What is the key concept addressed by the question?
· What type of thinking is required?
Gather Content
· What do you already know about bacterial cell walls? How does it relate to the question?
Choose Answer
· Given what you now know, what information and/or problem solving approach is most likely to produce the correct answer?
Reflect on Process
· Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
B. Pathogens often encase themselves in a gelatinous capsule.
Clarify Question
· What is the key concept addressed by the question?
o You need to determine which option best explains how bacterial cells avoid being detected by the host’s immune system.
· What type of thinking is required?
o This question is an “apply” question. You need to use your knowledge of bacterial anatomy and apply it to this new situation.
Gather Content
· What do you already know about bacterial cell walls? How does it relate to the question?
o Bacteria can be gram-positive, with a cell wall made of a thick layer of peptidoglycan (a lipopolysaccharide).
o They can also be gram-negative, with a cell wall made of a thin layer of peptidoglycan sandwiched between the plasma membrane and the outer membrane.
o The cell wall has several purposes. It protects the cell from damage. It also keeps the cell from bursting if it is put in a hypotonic solution. What do you know about the cell walls of pathogenic bacteria? What do they do to keep the hosts’ immune system from recognizing them?
Choose Answer
· Given what you now know, what information and/or problem solving approach is most likely to produce the correct answer?
o Pick any pathogenic bacterium you remember from class or the textbook. Does it have a cell wall? What is the cell wall made of? Read over the options. There are a couple you can cross off fairly easily. Then, review the information in the text to choose between the last couple options.
Reflect on Process
· Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
o This question asked you to explain how pathogenic bacteria can avoid the immune cells if the immune cells can detect peptidoglycan.
o If you got the correct answer, great job!
o If you got an incorrect answer, where did you get stuck?
· All bacteria have cell walls, but many pathogenic ones also have a gelatinous capsule. This capsule allows them to stick to surfaces and avoid detection. There is more information about this in your text.
You might also like to view...
Genetics is defined as the scientific study of ____
a. diseases b. DNA c. heredity d. chromosome structure e. cell structure
What are the signs of skin cancer that distinguish it from other skin irregularities?
What will be an ideal response?
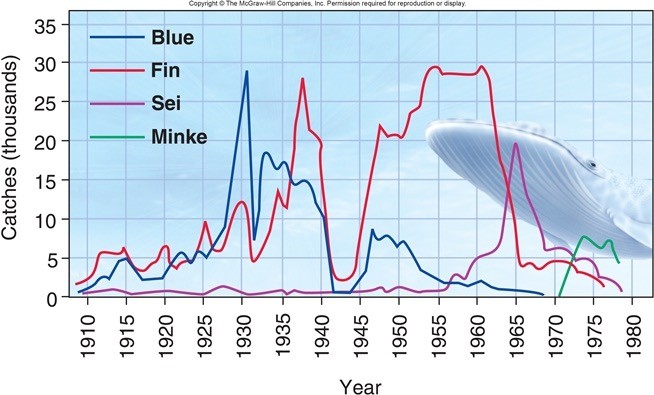 Fishing by humans has severely affected populations of many different marine species, including whales. Examine the figure above, making sure to note what each axis represents. What can best explain the pattern for minke whales?
Fishing by humans has severely affected populations of many different marine species, including whales. Examine the figure above, making sure to note what each axis represents. What can best explain the pattern for minke whales?
A. Minke whales were too difficult to catch until they become malnourished due to exploitation competition by other whales. B. Minke whale populations were overfished in the early 1900s, then recovered in the 1970s as their competitors were killed off. C. Minke whales are a new species that evolved during the 1960s as an ecological niche opened up. D. Commercial whalers did not pursue minke whales until the more valuable whale species had declined.
If the antenna complex did not exist in a particular plant mesophyll cell, what effect would that have on photosynthesis?
A. These cells would be unable to absorb any light energy. B. These cells would have a reduced capacity to generate glucose. C. There would be no expected effect on photosynthesis. D. These cells would be able to fix more carbon dioxide.