A copper-nickel alloy is used in a heat exchanger for a power plant that uses ocean water for cooling. One way to check the consistency of the alloy’s composition across batches of material is to determine the lattice parameter of the alloy. We know that copper and nickel are both FCC crystals and that copper and nickel form a limited-solid solution, and also that the lattice parameter of the alloy depends upon the composition. To determine the lattice parameter of the alloy, the angles of the diffraction peaks from a polycrystalline piece of the alloy are measured in an x-ray diffractometer with a cobalt x-ray tube. Cobalt is used because the cobalt K? radiation is of a lower energy than is the absorption edge in either copper or nickel, and no characteristic x-rays will be generated
in the copper and nickel. Also, the copper and nickel should be relatively transparent to the cobalt K? radiation.
With the cobalt K? radiation, the lowest angle intense peak is measured at 25.74°. The
lattice parameter of copper is 0.361 nm and for nickel it is 0.352 nm, and the wavelength of cobalt K? radiation is 0.1790 nm.
(a) What are the Miller indices of this peak, and what is the lattice parameter of this
copper-nickel mixture?
(b) Assuming that the lattice parameter varies linearly with composition in this alloy,
what is the percent of nickel and copper?

Solve for a:
a =1.732(0.2061 nm) = 0.357 nm
The peak must be the (111) peak for this gives a reasonable lattice parameter for the copper–nickel alloy that is in between the lattice parameters of copper and nickel.
(b) If the lattice parameter varies linearly with composition we can determine ratio of the change in the lattice parameter of the alloy relative to the difference in the copper and nickel lattice parameters and this is also the fraction of nickel (x).
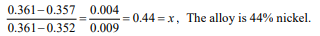
You might also like to view...
From what you know about astronomical units and light-years, how would you define a light-minute?
What will be an ideal response?
For a quantity of ideal gas, which of the following is constant?
a. PTV c. PT/V b. P/TV d. PV/T
Light from the Sun reaches Neptune in more than _____
A) 4 hours B) 5 hours C) 6 hours D) 7 hours
When space probe Voyager 2 passed by Saturn, its speed increased (but not due to firing its engines). What must have happened?
A) Saturn must have lost a tiny bit of its orbital energy. B) Voyager 2 must have dipped through Saturn's atmosphere. C) Saturn's rotation must have sped up slightly. D) Saturn must have captured an asteroid at precisely the moment that Voyager 2 passed by.