A 6.0-kg object moving 2.0 m/s in the positive x direction has a one-dimensional elastic collision with a 4.0-kg object moving 3.0 m/s in the opposite direction. What is the total kinetic energy of the two-mass system after the collision?
A. 30 J
B. 62 J
C. 20 J
D. 44 J
E. 24 J
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Bats can detect small objects such as insects that are of a size on the order of a wavelength. If bats emit a chirp at a frequency of 60 kHz and the speed of soundwaves in air is 330 m/s, what is the smallest size insect they can detect?
A. 1.5 mm B. 3.5 mm C. 5.5 mm D. 7.5 mm E. 9.8 mm
For a 10 mol mixture of air (8 mols nitrogen, N2, and 2 mols oxygen, O2) at 101 kPa, 20ºC, determine the mass concentration and the molar concentration of N2 and O2.
What will be an ideal response?
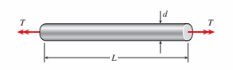
A brass rod of length L 5 0.75 m is twisted by torques T until the angle of rotation between the ends of the rod is 3.58. The allowable shear strain in the copper is 0.0005 rad. The maximum permissible diameter of the rod is approximately:
(A) 6.5 mm
(B) 8.6 mm
(C) 9.7 mm
(D) 12.3 mm
In the shape-memory effect in metals, the martensitic transformation must be _____________.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).