Expansionary fiscal policy tends to:
A. reduce both U.S. interest rates and U.S. capital inflows.
B. increase U.S. interest rates but reduce U.S. capital inflows.
C. reduce U.S. interest rates but increase U.S. capital inflows.
D. increase both U.S. interest rates and U.S. capital inflows.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Suppose one goal of the tax system was to achieve vertical equity. While people may disagree about what is "equitable," based on the marginal tax rates given for the two years, which of the following statements is true?
a. Vertical equity is possible in both years. b. Vertical equity is possible in 2009 but not in 2010. c. Vertical equity is not possible in 2009 but is possible in 2010. d. Vertical equity is not possible in either year.
Expressing the U.S. federal budget deficit as a percentage of Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
A) results in inflation-adjusted revenue and expenditure numbers. B) helps us understand the size of the deficit relative to the size of the economy. C) was useful through the 1980s, but is no longer helpful because both the deficit and real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) have grown so large. D) is only useful if the budget deficit is rising at an annual rate of more than 4 percent.
Fiat money differs from commodity money in that
a) only fiat money can be made legal tender b) fiat money has no intrinsic value c) fiat money is backed by gold d) only fiat money can serve as a unit of account e) only commodity money can serve as a store of value
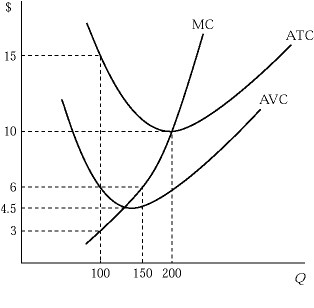
 Figure 6.3 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. The firm will stay in the market in the long run only if the market price is greater than or equal to:
Figure 6.3 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. The firm will stay in the market in the long run only if the market price is greater than or equal to:
A. $4.50. B. $6. C. $10. D. $15.