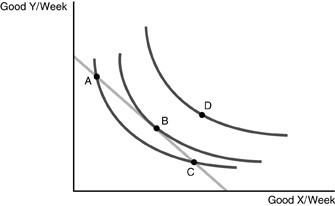
 Refer to the above figure. Given the indifference map and budget constraint represented above, what would make all possible points attainable for the individual to consume?
Refer to the above figure. Given the indifference map and budget constraint represented above, what would make all possible points attainable for the individual to consume?
A. a decrease in income
B. an increase in the price of Good Y
C. a decrease in the price of Good X
D. an increase in the price of Good X
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
The output level that occurs in any market that is in equilibrium:
a. is the quantity where the supply curve intersects the y-axis. b. is the quantity where the demand curve intersects the x-axis. c. is the quantity at an output level where buyers will pay more than suppliers require. d. is an output level where buyers will not pay as much as suppliers require. e. is the quantity where the demand and supply curves intersect each other.
Assume that foreign capital flows into a nation rise due to expected increases in stock market appreciation. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a fixed exchange rate system, what happens to the real risk-free interest rate and monetary base in the context of the Three-Sector-Model? a. The real risk-free interest rate falls and monetary base falls
b. The real risk-free interest rate rises and monetary base falls. c. The real risk-free interest rate and monetary base remain the same. d. The real risk-free interest rate falls and monetary base rises. e. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables.
As the tax on a good increases from $1 per unit to $2 per unit to $3 per unit and so on, the
a. tax revenue increases at first, but it eventually peaks and then decreases. b. deadweight loss increases at first, but it eventually peaks and then decreases. c. tax revenue always increases, and the deadweight loss always increases. d. tax revenue always decreases, and the deadweight loss always increases.
Referring to Figure 1.5, the opportunity cost of producing the second unit of pizza is 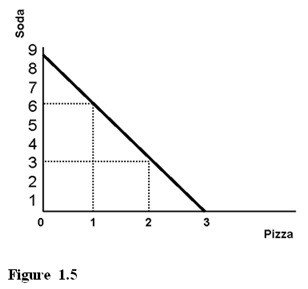
A. one unit of soda. B. six units of soda. C. three units of soda.