(a) Fill in table. (b) Using your own piece of graph paper, draw a graph of the firm's demand, marginal revenue, marginal cost, and average total cost curves. (c) Calculate the firm's total profit. (d) If the firm operates at optimum efficiency, how much will its output be? (e) If the firm were a perfect competitor, how much will its price be in the long run?
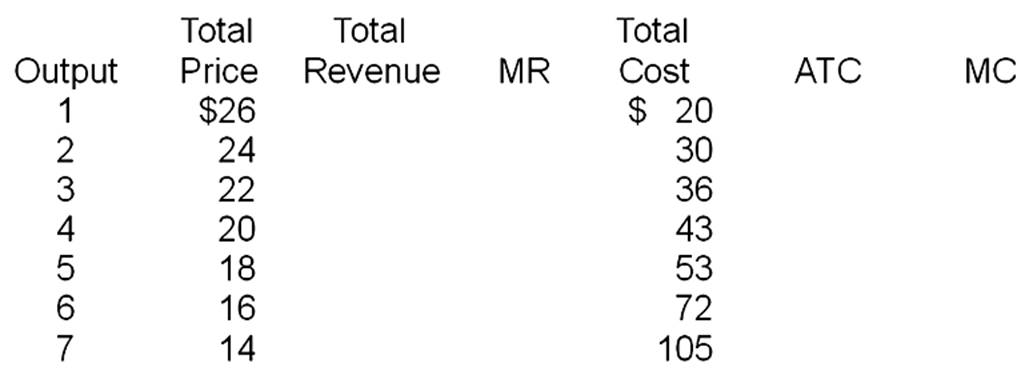
(a) 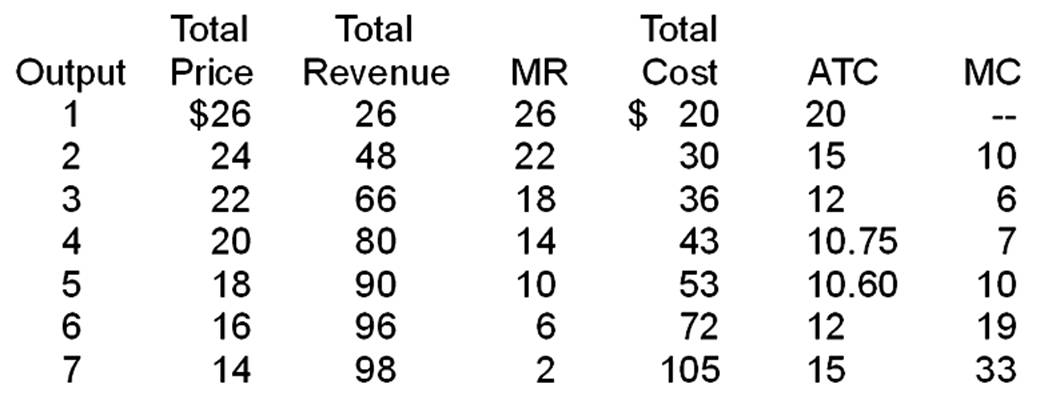
(b) 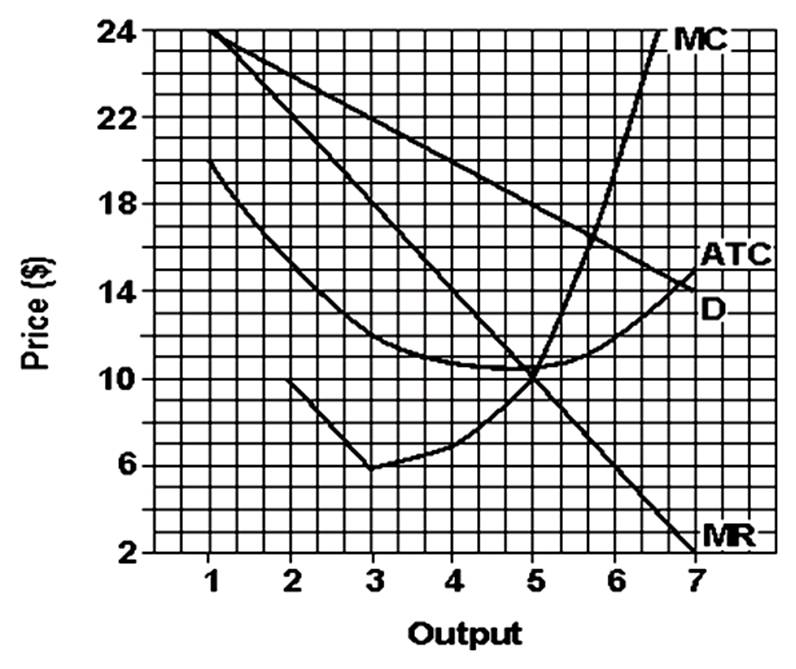
(c) There are two ways to calculate total profit:
(1) Total Profit = Total Revenue - Total Cost
= $90 - $53
= $37
(2) Total Profit = (Price - ATC) × Output
= ($18 - $10.60) × 5
= $7.40 × 5
= $37
(d) 5.05; (e) $10.58
You might also like to view...
If a sum of $15,000 is borrowed at 13% for a year, the interest paid by the borrower is ________
A) $750 B) $1,000 C) $1,950 D) $5,500
Suppose the economy is in a recession and the government decides it needs to reduce the budget deficit. Other things equal, this would tend to
A) shift the IS curve to the right. B) shift the IS curve further to the left. C) shift the MP curve further down. D) shift the MP curve up.
Which of the following is not included in GDP as part of government services?
A.) Social Security benefits. B.) Military equipment. C.) Highways and bridges. D.) Education.
If there were a market for pollution rights established by a public agency that determined the amount of pollution that the atmosphere or a body of water can safely absorb, and the agency sold these rights to polluters, we could expect that:
A. the price of these pollution rights would increase over time as the economy grows. B. there would be a shortage of pollution rights. C. there would be a black market for pollution rights. D. there would be a surplus of pollution rights.