All of the following are examples of goods for which external costs commonly exist EXCEPT
A. oil transportation.
B. cigarettes.
C. vaccinations.
D. automobiles.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
In the textual example, Muhammad Yunus was highly successful in his use of applying social incentives through group responsibility in order to maximize loan repayment rates. This success created an incentive for other banks to:
A. offer similar loans to the poor. B. go out of business. C. seek government action to ban group responsibility lending. D. avoid catering to a high risk group.
Instead of a uniform standard, suppose each firm faces a volume-based, marginal effluent fee (MEF) of $90. How much will each firm abate?
Among the identified point sources contributing to the pollution of Puget Sound are Dow Chemical (D) and Chevron (C). Each firm's cost functions are shown below. MACD = 2.5AD MACC = 3.75AC TACD = 1.25AD2 TACC = 1.875AC2 To meet the effluent limits under the Clean Water Act, each firm has an NPDES permit to release some fixed amount of effluents, so each must abate 30 units.
Which of the following examples reflects the liquidity trap?
a. After a bank receives additional reserves, it collects interest on those funds rather than loaning them. b. After receiving additional reserves, a bank invests large sums in a bull market. c. After a bank receives additional reserves, the number of loans it makes increases significantly. d. After receiving additional reserves, a bank uses half of them for investments.
Refer to the graph below with three demand curves. An "increase in quantity demanded" would be illustrated by a change from:
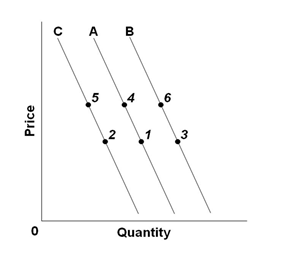
A. Point 4 to point 6
B. Point 5 to point 1
C. Point 4 to point 1
D. Point 2 to point 5