Describe four forms of affirmative action
What will be an ideal response?
1. A program may consist of policies to ensure that all potentially qualified workers know about a particular job opening. This ensures that everyone has equal information and equal access to the application process.
2. An interpretation that suggests that if two applicants have the same qualifications for a particular job, but one applicant happens to be from a disadvantaged class (usually due to race or gender), the job should be offered to the disadvantaged candidate.
3. A suggestion that the labor pool should be representative of the community of qualified applicants. This helps ensure that the proportion of minorities does not drop too low.
4. A quota, which is the most restrictive form of affirmative action, sets numerical targets companies must meet for the hiring of minorities.
You might also like to view...
The analysis is externally valid if
A) the statistical inferences about causal effects are valid for the population being studied. B) the study has passed a double blind refereeing process for a journal. C) its inferences and conclusions can be generalized from the population and setting studied to other populations and settings. D) some committee outside the author's department has validated the findings.
When Brenda was in college, she worked part-time delivering pizzas and she ate five boxes of macaroni and cheese per week. After graduation, she became a high school teacher and ate only two boxes of macaroni and cheese per week. From this information,
a. macaroni and cheese is a normal good for Brenda b. the law of demand applies to macaroni and cheese for Brenda c. macaroni and cheese are substitute goods d. macaroni and cheese is an inferior good for Brenda e. Brenda's income elasticity of demand for macaroni and cheese is positive
In general, it can be said that leisure is a "free good."
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Player 1 and Player 2 are playing a game in which Player 1 has the first move at A in the decision tree shown below. Once Player 1 has chosen either Up or Down, Player 2, who can see what Player 1 has chosen, must choose Up or Down at B or C. Both players know the payoffs at the end of each branch.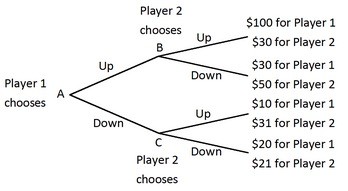 What is the equilibrium outcome of this game?
What is the equilibrium outcome of this game?
A. Player 1 and Player 2 both choose Down. B. Player 1 chooses Up and Player 2 chooses Down. C. Player 1 chooses Down and Player 2 chooses Up. D. Player 1 and Player 2 both choose Up.