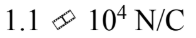Aluminum Rod#1 has a length L and a diameter d. Aluminum Rod#2 has a length 2L and a diameter 2d. If Rod#1 is under tension T and Rod#2 is under tension 2T, how do the changes in length of the two rods compare?
a. They are the same.
b. Rod#1 has double the change in length that Rod#2 has.
c. Rod#2 has double the change in length that Rod#1 has.
d. Rod#1 has quadruple the change in length that Rod#2 has.
e. Rod#2 has quadruple the change in length that Rod#1 has.
a
You might also like to view...
A charge of 8.0 pC is distributed uniformly on a spherical surface (radius = 2.0 cm), and a second charge of ?3.0 pC is distributed uniformly on a concentric spherical surface (radius = 4.0 cm). Determine the magnitude of the electric field 5.0 cm from the center of the two surfaces
a. 14 N/C b. 11 N/C c. 22 N/C d. 18 N/C e. 40 N/C
Can an element decay "backward" in the periodic table, to a lower atomic number?
A) No, in fact elements cannot alter their atomic number by radioactive decay. B) No, but an element can decay to a higher atomic number. C) Yes, by beta decay. D) Yes, by alpha decay. E) Yes, radioactive decay always causes elements to decay to a lower atomic number.
What elements do the symbols H, O, C, and N stand for?
a. hydrogen, ozone, carbon, nitrogen b. hydrogen, oxygen, chlorine, nitrogen c. hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, natrium d. hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, nitrogen e. none of the above
What is the magnitude of the electric field 30.0 cm from a point charge of 0.35 ?C?
a. 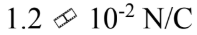
b. 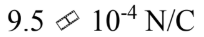
c. 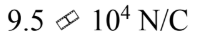
d. 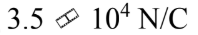
e.