Calorimetry: A person is walking outdoors on a cold day when the temperature is -20°C. He is breathing at the rate of 16 breaths per minute, and each time he breathes in he inhales 0.0050 m3 of air. At what rate does he lose heat from breathing if the air in his lungs is heated to body temperature (37°C) before it is exhaled? The specific heat of air is 1020 J/kg ? K and the density of air is 1.29 kg/m3.
A. 60 W
B. 90 W
C. 100 W
D. 150 W
E. 300 W
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
If the universe is closed and finite, then
a. the universe will expand forever b. the universe has a center c. the universe has an edge d. none of the above
Two blocks are made of the same material, but one has twice the volume of the other block. Which block will have the greater shear modulus?
A) It will be the same for both of them. B) the larger one C) the smaller one
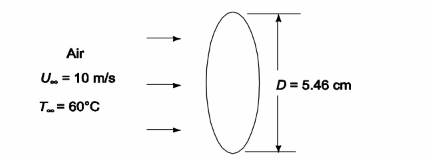
if the extrusion cross-section is elliptical with the major axis normal to the air flow and same mass per unit length. The major axis of the elliptical cross-section is 5.46 cm and its perimeter is 12.8 cm
GIVEN
• A long elliptical copper extrusion in an air stream
• Initial temperature (To) = 400°C
• Air Temperature (T?) = 50°C
• Air velocity (V?) = 10 m/s
• Surface emissivity (?) = 0.9
• Elliptical cross-section with major axis normal to the air flow
• Length of the major axis of the ellipse (D) = 5.46 cm = 0.0546 m
• Perimeter of ellipse (P) = 12.8 cm = 0.128 m
• Same mass per unit length as Problem 6.9
FIND
• The time (t) required for the center of the copper to cool to 100°C
ASSUMPTIONS
• Air flow is perpendicular to the axis of the extrusion
• Variation of the copper properties with temperature is negligible
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the initial and final film temperature of 150°C
Thermal conductivity (ka) = 0.0339 W/(m K) Kinematic viscosity (?) = 29.6 × 10–69 m2/s Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71
Thermal conductivity (k) = 386 W/(m K) at 250°C Density (?) = 8933 kg/m3 at 20°C Specific heat (c) = 383 J/(kg K) at 20°C
The Sun rotates ________ at its equator compared to near its poles.
A. slower B. backwards C. the same D. faster