A 2.0-kg block slides on a frictionless 25° inclined plane. A force of 4.6 N acting parallel to the incline and up the incline is applied to the block. What is the acceleration of the block?
a. 1.8 m/s2 up the incline
b. 2.3 m/s2 up the incline
c. 6.6 m/s2 down the incline
d. 1.8 m/s2 down the incline
e. 2.3 m/s2 down the incline
D
You might also like to view...
Why is the temperature at the region of a sunspot cooler than the photosphere?
a. They are holes in the photosphere that reveal the lower temperature gases in the deeper layers. b. They represent points where streams of cool gas from the corona lower the temperature in those regions of the photosphere. c. Powerful magnetic fields in the sunspots act upon the atoms of the photosphere to prevent them from emitting light. d. Powerful magnetic fields inhibit the convective flow of the gases of the photosphere downward, allowing them to cool for longer than would normally be permitted.
The rapid rotation and large size of Jupiter causes _______________ in its atmosphere
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Which of the following are not a common depositional feature of shoreline topography?
a. Barrier islands b. Pocket beaches c. Sea arches d. Spits
Force on a Wire: A wire in the shape of an "M" lies in the plane of the paper. It carries a current of 2.0 A, flowing from A to E. It is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 0.85 T in the same plane, directed as shown on the right side of the figure. The figure indicates the dimensions of the wire. Note that AB is parallel to DE and to the baseline from which the magnetic field direction is measured. What are the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on this wire?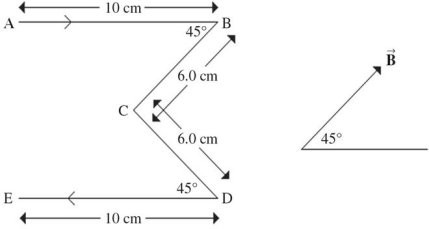
A. 0.40 N perpendicular out of the page B. 0.10 N perpendicular into the page C. 0.40 N perpendicular into the page D. 0.10 N perpendicular out of the page E. 0.20 N perpendicular out of the page