The driver of a motorboat that can move at 10 m/s in still water wishes to travel directly across a river in which the current flows at 5.0 m/s
(a) At what angle, measured from the upstream direction, should the driver head the boat? (b) How many minutes will it take to cross the river if it is 1.6 km wide at that point?
(a) 60° (b) 3.1 min
You might also like to view...
What is the velocity of the wave in the above figure?
The following figure is a graph of a wave at a fixed position.

The following figure is a graph of the same wave at a fixed time.
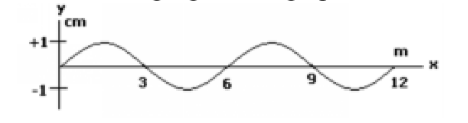
A. 150 m/s
B. 200 m/s
C. 250 m/s
D. 300 m/s
E. 450 m/s
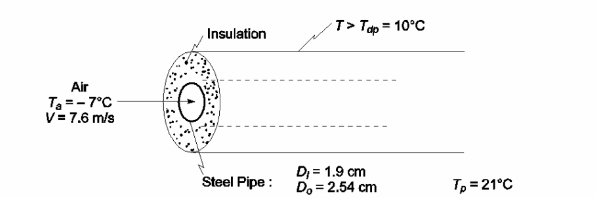
A 2.54-cm-OD, 1.9-cm-ID steel pipe carries dry air at a velocity of 7.6 m/s and a temperature of –7°C. Ambient air is at 21°C and has a dew point of 10°C. How much insulation with a conductivity of 0.18 W/(m K) is needed to prevent condensation on the exterior of the insulation if h = 2.4 W/(m2 K) on the outside?
GIVEN

FIND
Thickness of insulation (t) required to prevent condensation
ASSUMPTIONS
Steady state
Flow is fully developed
Pipe surface temperature can be considered uniform and constant
Radiation heat transfer to the insulation is negligible or included in ch ? Pipe is 1% carbon steel
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for dry air at –7°C by extrapolation
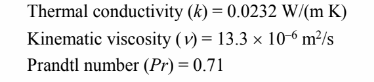
the thermal conductivity of 1% carbon steel (ks) = 52 W/(m K)
Binding energy per nucleon in a nucleus is
A. the same for all nuclei. B. the greatest for the largest nuclei. C. the greatest for the smallest nuclei. D. the greatest for medium-sized nuclei.
The constant G that appears in the equation F = Gm1m2/r2 is
a. smaller on the Moon than on Earth. b. the force of gravity. c. equal to 9.8 m/s2. d. the acceleration due to gravity. e. equal to 6.67 × 10^-11 Nm2/kg2.