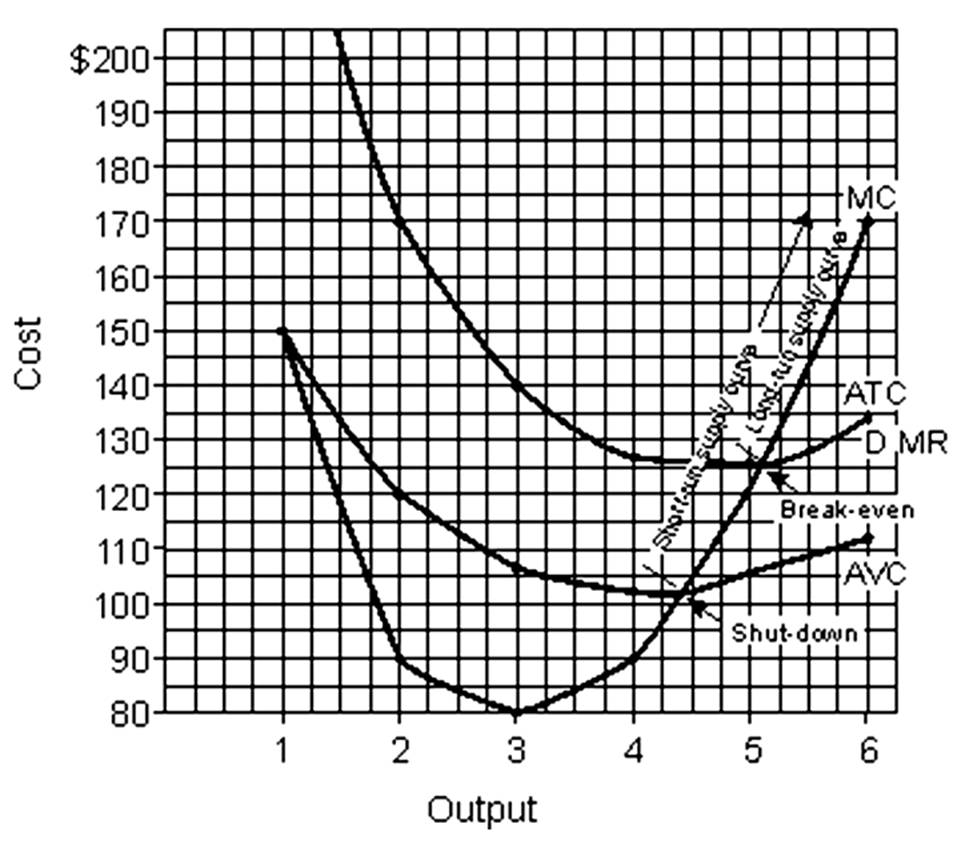
This problem should be done in four steps. First, fill in the table directly below. Assume that fixed cost is $100 and price is $130. Second, on the graph paper draw the graphs of the firm's demand, marginal revenue, average variable cost, average total cost, and marginal cost curves. Be sure you label the graph correctly. Indicate the firm's short-run and long-run supply curves, and the break-even and shutdown points. Third, calculate total profit in the space below and then answer questions A through D. Fourth, complete the second table.
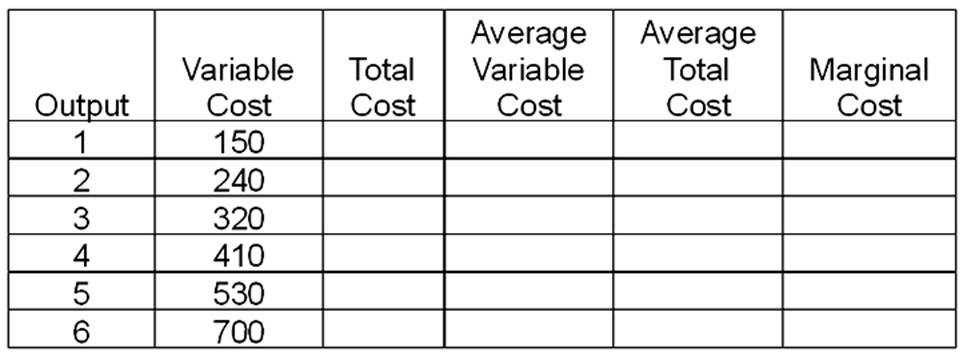
A. The minimum price the firm would accept in the short run would be $___________.
B. The minimum price the firm would accept in the long run would be $___________.
C. The output at which the firm would operate most efficiently would be ___________.
D. The output at which the firm would maximize profits would be ___________.

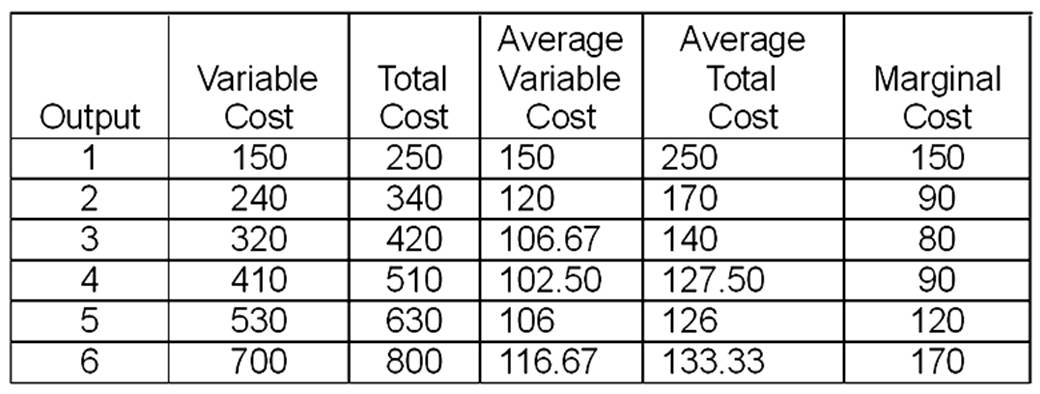
Total Profit = (price - ATC) × output
= ($130 - $126) × 5.23
= $4 × 5.23
= $20.92
a. $102 (must be under $102.50)
b. $125.80 (must be under $126)
c. 5.15
d. 5.23

You might also like to view...
In the labor market, an increase in labor productivity ________ the real wage rate and ________ the level of employment
A) raises; increases B) raises; decreases C) lowers; increases D) lowers; decreases
Population increases are the limiting factor in the growth process in
A) classical growth theory. B) neoclassical growth theory. C) the new growth theory. D) real growth theory.
A monopoly:
a. can increase price and increase output at the same time. b. can charge any price it wants and still sell all of its output. c. can sell any output it produces provided it accepts the market price. d. must lower price in order to increase output. e. faces a perfectly elastic demand curve.
The United States' involvement in World War II caused
a. both the aggregate demand curve and aggregate supply curve to shift outward, causing GDP to increase and the price level to decrease b. both the aggregate demand curve and aggregate supply curve to shift inward, causing GDP to increase and the price level to decrease c. the aggregate demand curve to shift inward and the aggregate supply curve to shift outward, causing both GDP and the price level to increase d. the aggregate demand curve to shift outward and the aggregate supply curve to shift inward, causing both GDP and the price level to increase e. aggregate demand to initially shift out, then reverse, leaving the economy at equilibrium