The perfectly competitive firm:
A) makes its profit-maximizing decision only on the basis of output.
B) faces a downward-sloping demand function.
C) can influence market price only in a downward direction.
D) cannot earn any economic profits because it faces a horizontal demand curve.
A
You might also like to view...
What will happen if the institutions in an economy transform from inclusive to extractive?
A) The return-to-entrepreneurship schedule will shift rightward and the opportunity cost to entrepreneurship will decrease. B) The return-to-entrepreneurship schedule will shift leftward and the opportunity cost to entrepreneurship will decrease. C) The return-to-entrepreneurship schedule will shift leftward and the opportunity cost to entrepreneurship will increase. D) The return-to-entrepreneurship schedule will shift rightward and the opportunity cost to entrepreneurship will increase.
A monopolistically competitive firm has ________ power to set the price of its product because ________
A) no; there are no barriers to entry B) some; there are barriers to entry C) no; of product differentiation D) some; of product differentiation
If U.S. citizens decide to save a larger fraction of their incomes, the real interest rate
a. decreases, the real exchange rate of the dollar depreciates, and U.S. net capital outflow increases. b. decreases, the real exchange rate of the dollar appreciates, and U.S. net capital outflow decreases. c. increases, the real exchange rate of the dollar appreciates, and U.S. net capital outflow decreases. d. increases, the real exchange rate of the dollar depreciates, and U.S. net capital outflow increases.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 23.11 below to answer the question(s) that follow.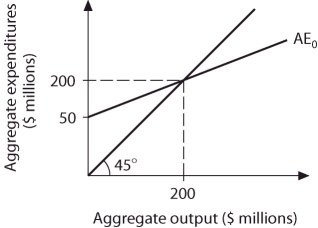 Figure 23.11Refer to Figure 23.11. Equilibrium aggregate output will increase to $250 million if the
Figure 23.11Refer to Figure 23.11. Equilibrium aggregate output will increase to $250 million if the
A. multiplier increases to 8. B. MPC increases to 0.8. C. MPS increases to 0.8. D. all of the above.