The highest Herfindahl-Hirschman Index
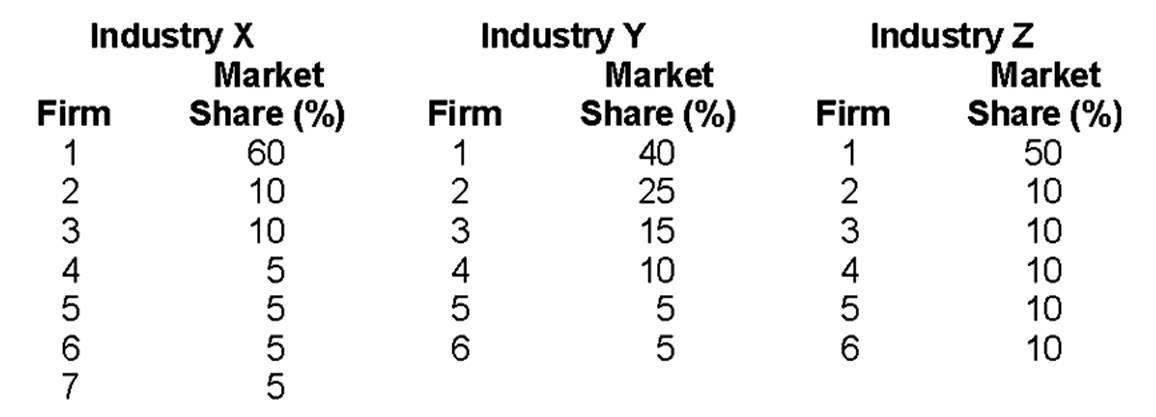
A. is in Industry X.
B. is in Industry Y.
C. is in Industry Z.
D. cannot be determined.
A. is in Industry X.
You might also like to view...
Refer to Goods X and Y. If the indifference curves are downward sloping straight lines (rather than convex curves), then we can conclude that
Assume that good X is on the horizontal axis and good Y is on the vertical axis in the consumer-choice diagram. PX denotes the price of good X, PY is the price of good Y, and I is the consumer's income. Unless otherwise stated, the consumer's preferences are assumed to satisfy the standard assumptions. a. X does not affect the individual’s utility. b. Y does not affect the individual’s utility. c. both X and Y affect the individual’s utility. d. neither good affects the individual’s utility.
Which of the following explains the Phillips curve trade-off?
a. workers' focus on job security as the economy expands rapidly b. firms weaken their resistance to wage pressure during periods of rapid economic growth c. firms' ability to pass along higher wage rates in the form of higher prices during recessions d. an unusual increase in resource supply e. workers' insistence on wage increases during recessions to compensate for unemployment
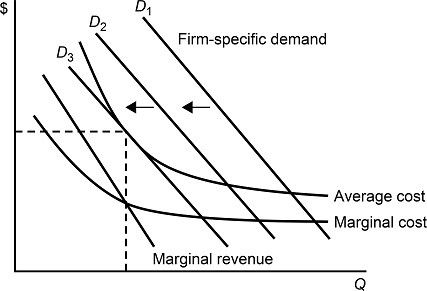
 Figure 8.3 shows demands and costs for a monopolistically competitive firm. When the firm's demand curve shifts from D1 to D2 and to D3:
Figure 8.3 shows demands and costs for a monopolistically competitive firm. When the firm's demand curve shifts from D1 to D2 and to D3:
A. the firm's economic profit remains the same. B. the firm's marginal revenue at the profit-maximizing output level is decreasing. C. the firm's marginal cost at the profit-maximizing output level is increasing. D. the firm's average cost at the profit-maximizing output level is decreasing.
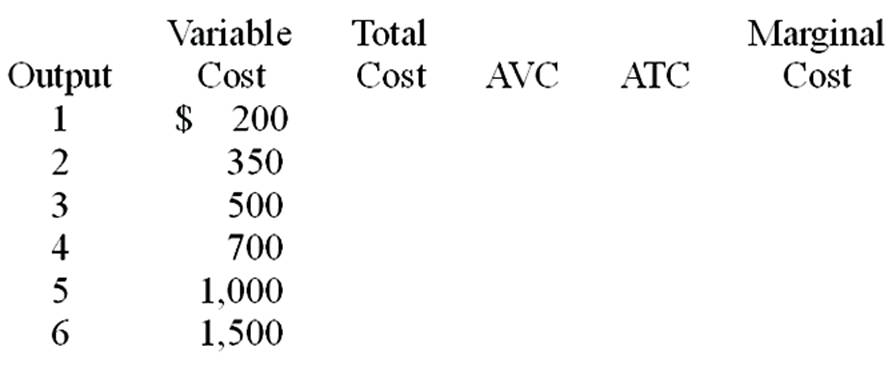
Fill in the table. Assume the fixed cost is $300.