Air enters an uninsulated nozzle at 5 m/s, 500 kPa, and 50°C. The cross-sectional area of the inlet is 0.0002 m2. The air exits at a velocity of 120 m/s and a temperature of 48°C. Determine the heat transfer rate for the nozzle.
Given: Air, P1 = 500 kPa; T1 = 50°C = 323 K; V1 = 5 m/s; A1 = 0.0002 m2; V2 = 120 m/s; T2 = 48°C = 321 K
What will be an ideal response?
For a nozzle, assume steady –state, steady-flow single-inlet, single-outlet flow, and assume that W?=?pe=0
As the temperature change is small, we will consider air to be an ideal gas with constant specific heats: h2 – h1 = cp (T2 – T1)
These assumptions result in the first law being (State 1 is inlet, State 2 is outlet)
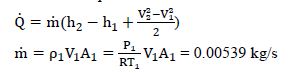
where R = 0.287 kJ/kg-K. For air, take cp = 1.005 kJ/kg-K
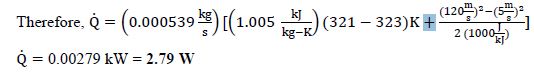
This is a very small heat transfer rate, but so is the mass flow rate of the nozzle. A larger mass flow rate would cause the heat transfer rate to become larger.
You might also like to view...
?If the reading on the vernier height gage is 16.88 mm, which vernier scale graduation most closely coincides with a main scale graduation?
A. ?19 B. ?12 C. ?4 D. ?10
? Identify and state the historical significance of Jane Addams.
What will be an ideal response?
Which of the following is NOT a modified stem?
a. rhizome c. cortex b. tuber d. bulb
The ram diameter of a certain cylinder is 2.50 inches, while the cylinder diameter is 5.00 inches. If the pump that actuates this cylinder is rated at 4.5 GPM at system pressure, what is the contracting speed of the cylinder, in inches per second?
What will be an ideal response?