A way to demonstrate to yourself that light is a wave is by
A) allowing light from two flashlights to strike a screen.
B) observing light as it bends while passing from air into water.
C) using a prism to separate light into its various components.
D) allowing light to reflect from a mirror.
E) observing the light that passes through a narrow space between your fingers.
E
You might also like to view...
An air-cooled low-pressure-steam condenser is shown in following figure.
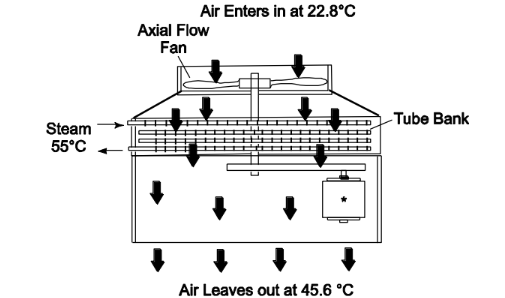
An air-cooled low-pressure-steam condenser is shown in following figure.
The tube bank is four rows deep in the direction of air flow and there are total of 80 tubes. The tubes have ID = 2.2 cm and OD 2.5 cm and are 9-m-long with circular fins on the outside. The tube-plus-fin area is 16 times the bare tube area (i.e., the fin area is 15 times the bare tube area, neglect the tube surface covered by fins). The fin efficiency is 0.75. Air flows past the outside of the tubes. On a particular day, the air enters at 22.8°C and leaves at 45.6°C. The air flow rate is 3.4 × 105 kg/h. The steam temperature is 55°C and has a condensing coefficient of 104 W/(m2 K). The steam-side fouling coefficient is 104 W/(m2K). The tube wall conductance per unit area is 105 W/(m2K). The air-side fouling resistance is negligible. The air-side-film heat transfer coefficient is 285 W/(m2K). (Note this value has been corrected for the number of transverse tube rows.) (a) What is the log-mean temperature difference between the two streams? (b) What is the rate of heat transfer? (c) What is the rate of steam condensation? (d) Estimate the rate of steam condensation if there were no fins.
GIVEN
• The condenser shown above
• Number of tubes (N) = 80 and number of rows (Nr) = 4 (in air flow direction)
• Tube diameters Di = 2.2 cm = 0.022 m Do = 2.5 cm = 0.025 m
• Tube length (L) = 9 m
• Air temperature Ta,in = 22.8°C Ta,out = 45.6°C
• Air flow rate m a= 3.4 × 105 kg/h = 94.4 kg/s
• Steam temperature = 55°C (constant)
• Fin area = 15 (tube area)
• Fin efficiency (?f) = 0.75
• Steam side
Transfer coefficient h i= 104 W/(m2 K)
Fouling coefficient (1/Ri) = 104 W/(m2 K)
• Tube wall conductance per unit area (1/Rk) = 105 W/(m2 K)
• Air side: Transfer coefficient h o= 285 W/(m2 K)
• Fouling resistance on the air side is negligible
FIND
(a) The log-mean temperature difference(LMTD)
(b) The rate of heat transfer (q)
(c) The rate of steam condensation m
(d) Estimate the rate of steam condensation if there were no fins 2cm
ASSUMPTIONS
• Air side transfer coefficient is the same with or without fins
• Tube surface covered by the fins is negligible
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for dry air at the average temperature of 34.2°C,
the specific heat (cpa) = 1013 J/(kg K),
for steam at a saturation temperature of 55°C,
the heat of vaporization (hfg) = 2600 (kJ/kg)
A sealed container holds 0.020 moles of nitrogen (N2) gas, at a pressure of 1.5 atmospheres and a temperature of 290 K
The atomic mass of nitrogen is 14.0 g/mol. The Boltzmann constant is 1.38 × 10-23 J/K and the ideal gas constant is R = 8.314 J/mol · K = 0.0821 L · atm/mol · K. The mass density of the gas is closest to A) 0.90 kg/m3. B) 1.3 kg/m3. C) 1.8 kg/m3. D) 2.2 kg/m3. E) 2.6 kg/m3.
State Kepler's Third Law of Orbital Motion
What will be an ideal response?
Power: A 100%-efficient engine is being used to raise a 89-kg crate vertically upward at a steady rate. If the power output of the engine is 1620 W, how long does it take the engine to lift the crate a vertical distance of 18.7 m? Friction in the system is negligible.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).